PMBOK 6th edition: A guide to better project management
Reading time: about 7 min
Topics:
What is PMBOK?
PMBOK, or the Project Management Body of Knowledge, is a collection of standards, best practices, and procedures for planning and executing on projects successfully. It was originally published by PMI in 1996 and is now in its 6th edition.
If you’ve ever worked on a team tasked with a goal of completing a project within a set timeframe, you’ve witnessed the importance of effective project management. You need all the tools and resources you can get to help you take your project across the finish line.
Because various types of projects, regardless of scale or complexity—constructing a home, designing a rocket ship, organizing a prom, producing a film, etc.—all share similar steps, over time project managers and thought leaders in this space have identified key overlapping steps. These steps have been categorized into a collection of standards, best practices, and procedures referred to as the Project Management Body of Knowledge, or in shorthand, “PMBOK.”
Originally published by PMI in 1996 and now in its 6th edition, the PMBOK still guides project managers to successful outcomes. Learn more about PMBOK project management.
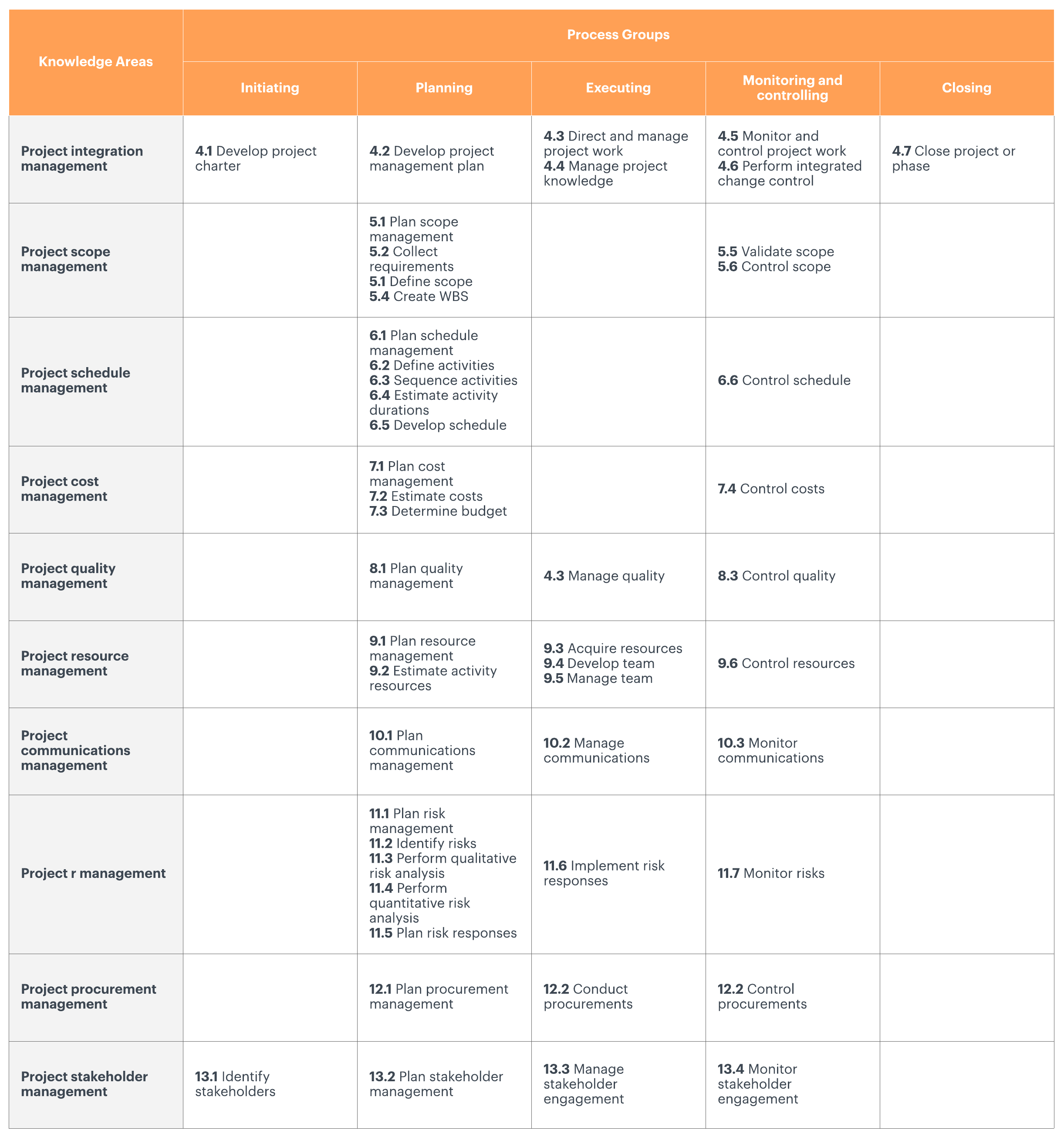
Get a closer look at our PMBOK matrix.
What is PMBOK?
Virtually all industries require some level of project management. But as the project management profession has developed with the advent of big industry, technology, commerce, and the major infrastructures that support them, the PMBOK developed as a consolidated methodology on how to approach project management. Created and updated by the Project Management Institute, the PMBOK is a manual that identifies the repeated features of the project management process.
A good way of understanding the PMI PMBOK is by comparing it to the scientific method. In the same way that scientists of unrelated disciplines may all conduct experiments according to the scientific method—make observations, form a hypothesis, design and perform experiments, accept or modify hypothesis, draw a conclusion and develop it into a law or theory—project managers can use the PMBOK to ensure that they are building upon the processes of successful past project management, or even use it as a way to refine their own project management processes.
PMBOK process groups
The most recent version of PMBOK identifies 49 processes for project management, which are broken down into five PMBOK process groups:
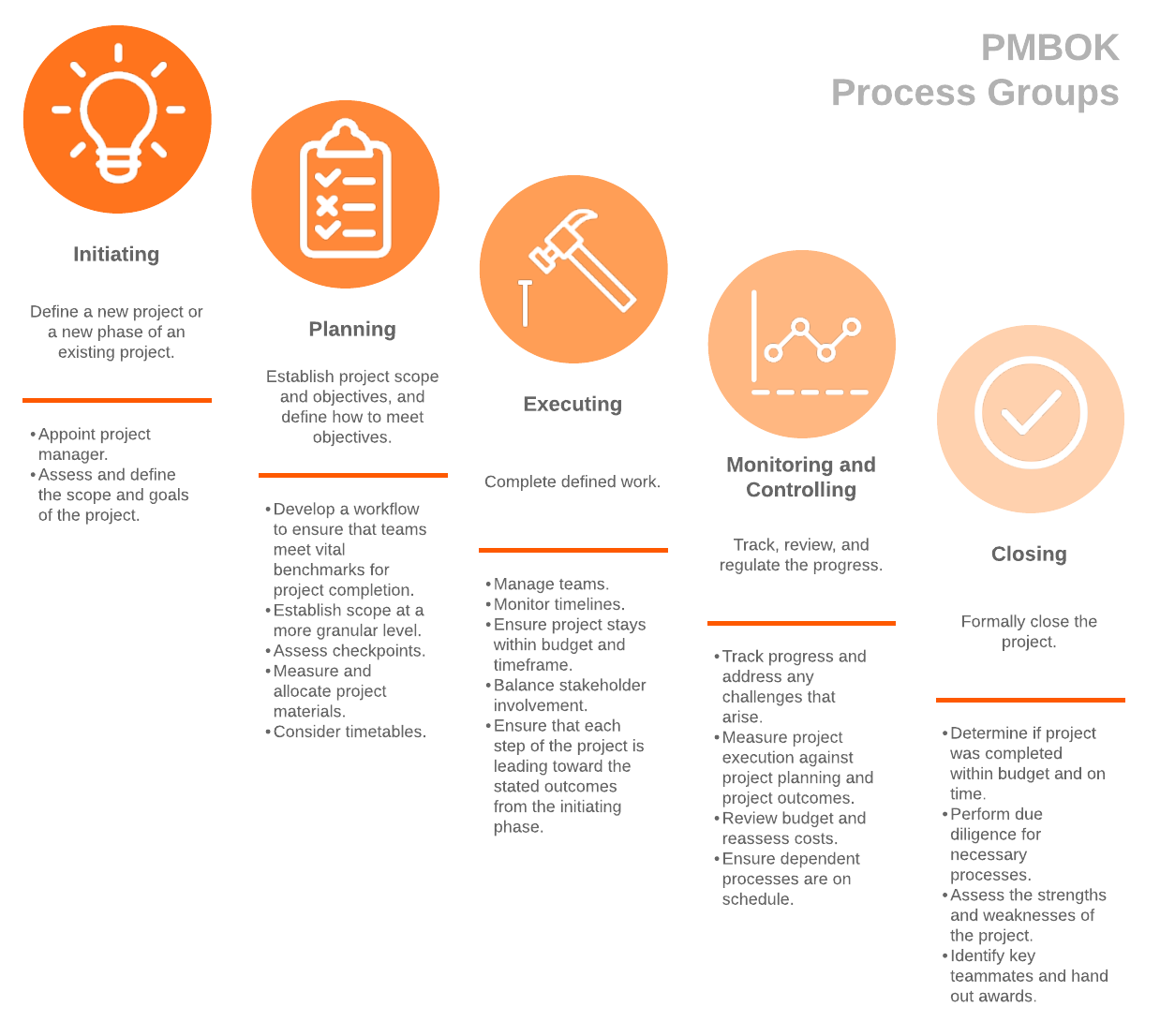
1. Initiating
In this part of the process, project managers define the scope and goals of the project—by establishing what they hope the project will accomplish, they can more easily gain buy-in.
During this phase, the feasibility and potential ROI of a project may be tested through a feasibility study, and stakeholder signoff is the ultimate goal. This step in project planning is crucial, as stakeholders have to give their approval of the project charter, ensuring that the finished result meets the goals of the organization involved.
This is also the point in the process where a project manager is appointed, as well as a succession plan in the event project management needs to change mid-project.
2. Planning
During the planning phase, project managers develop a project management plan to ensure that teams meet vital benchmarks for project completion. They establish the project scope at a more granular level, measuring and allocating project materials and establishing risks, timelines, milestones, and budget.
The planning phase expands upon the initiation phase, laying out exactly what is needed to achieve project completion—with variables like cost and personnel identified. At this point, project managers would create a work breakdown structure (WBS), and they might use timelines or PERT charts to account for all activities and dependencies to develop a schedule.
3. Executing
Most think of the executing phase as the most vital, when the truth is that execution, while important, is a crucial time and energy drain without the right planning. The project plan you’ve established in the last phase will guide you to project completion.
Execution involves managing teams, monitoring timelines, and staying within budget and timeframe. The best project managers also balance stakeholder involvement, ensuring that each step of the project is leading toward the stated outcomes from the initiating phase.
4. Monitoring and controlling
Once the project is moving, project managers have to track progress and address any challenges that arise to complete the project according to expectations. This phase revolves around metrics—acute analysis of project execution measured against project planning and project outcomes is the guiding focus. Considering budget, reassessing costs, and ensuring dependent processes are on schedule are all crucial parts of this phase.
Project processes are measured by KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), giving project managers key decision-making information on project deliverables and time, money, and energy expenditure and helping them determine if any workflows need to be updated.
5. Closing
At the close of a major project, the biggest considerations are whether the project was completed within budget and whether the project was completed on time. A successful project closing also involves the project manager performing due diligence to make sure all processes have ceased and aren’t wasting any additional resources, like canceling shipments of excess material or returning any rented equipment.
Another vital part of project closing mentioned in the PMBOK is assessing the strengths and weaknesses of the project: Which processes worked well? Which areas needed improvement, and how will they be optimized in the future?
The answers to these questions are essential to creating more effective workflows. The best project managers will take it a step further by identifying key teammates and even giving out awards for performance. This seemingly small step has huge payoffs: Everyone wants to feel valued for their hard work and contribution, and public recognition can be a valuable motivator for future teams.
Learn more about the common PMBOK project phases and see how your team can complete projects more efficiently.
PMBOK knowledge areas
In addition to the five process groups, the PMBOK 6th edition organizes processes into ten knowledge areas:
1. Project integration management includes tasks that hold the whole project together, decompartmentalizing the steps and requirements of successful project completion.
2. Project scope management helps project managers define the work and deliverables that will be required to complete the project.
3. Project time management involves resource efficiency. Project managers must make sure that teammates are completing dependent tasks on time in order to keep the whole project on track.
4. Project cost management begins by forecasting the cost of each step of a project and even including budgeting for mishaps or compensating for any foreseeable obstacles. But the most important objective is staying within a stated budget.
5. Project quality management safeguards against subpar deliverables by establishing quality standards at each step of the project.
6. Project resource management can include hiring the right teammates, assigning the right teammates, and, in some cases, training teammates to perform new tasks.
7. Project communications management involves setting up a communications plan and maintaining the necessary lines of communication.
8. Project risk management involves assessing and preparing for potential risks and must be carried out through every step of the project, including when/if plans change mid-project.
9. Project procurement management means administering all of the planning and execution of hiring personnel, purchasing materials, creating statements of work with contractors, etc.
10. Project stakeholder management involves everything from determining stakeholders to assessing the role and desired outcome on the project and setting clear expectations between stakeholders and all personnel involved.
See the image below for a complete overview.
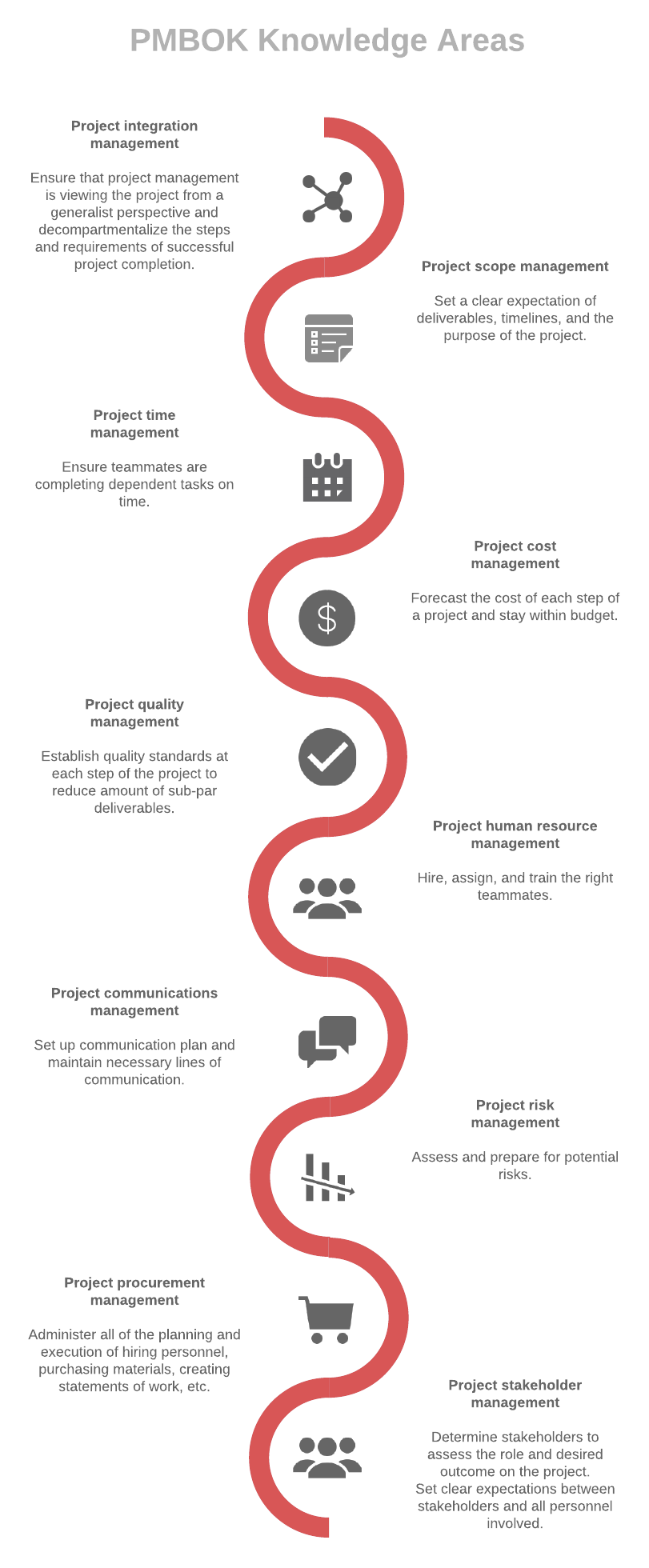
From constructing the Great Pyramids of Giza to releasing a new app, all successful project management requires intention and a framework in order to go from concept to completion. The Project Management Book of Knowledge provides just that framework and is an invaluable tool for experienced and burgeoning project managers alike.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
Top 6 reasons why project management is important
Project management is more than tracking deadlines—it can help your org meet deadlines and quality requirements in a world where 50% of projects fail.
What is a workflow? Benefits and examples of repeatable processes
Ensure that important processes are completed the right way, every time. In this article, we will explain why your business needs efficient workflows and show you some workflow examples to help you get started.
Workflow automation: How to get started
Workflow automation is one way to accelerate optimization throughout your company, reducing human error and redundancy. Learn how to locate processes in your organization that can be automated and how to automate those processes.
Understanding the difference between project management and change management
What is project management? What is change management? These terms are often confused, but you will likely need both to handle that changes that drive success. Learn the differences between project and change management, and see how to incorporate these methods at your company.
