
Advantages of PERT charts vs. Gantt charts
Reading time: about 6 min
PERT chart vs Gantt chart differences
PERT charts: Utilized before a project begins to plan and determine the duration of each task
Gantt charts: Used while a project is happening to break projects into smaller tasks and highlight scheduling constraints
Only 29% of projects are completed on time. And it’s no surprise why. With every project involving hundreds of moving parts, that’s a lot of information and deadlines to plan and track—leaving many managers struggling to stay on top of things. Yet, being able to clearly scope out your projects is critical to managing resources and ensuring projects are delivered on time and on budget.
That’s where project management tools like PERT charts and Gantt charts can help.
PERT charts and Gantt charts help teams visualize, plan, and manage complex projects
This post outlines the differences between PERT and Gantt charts including when it's appropriate to use each chart and how you can make your own.
What is a PERT chart?
PERT stands for Program Evaluation and Review Technique. A PERT chart illustrates a project as a network diagram—visualizing the logical and sequential relationship between project tasks. The U.S. Navy created this tool in the 1950s to simplify planning and scheduling complex projects as they developed the Polaris missile (and time was of the essence—this was during the Cold War, after all).
Project managers use PERT charts to gauge the minimum time necessary to complete the project, analyze task connections, and assess project risk. PERT is most useful in large-scale projects where time is the major factor rather than cost as the technique provides estimates based on optimistic, pessimistic, and expected timelines. PERT charts make it easy to visualize and organize complex projects illustrating the dependencies between each step in the project.

When project managers should use PERT Charts
PERT charts are best utilized by project managers at the beginning of a project to ensure that it is accurately scoped. By averaging three timeline estimates (optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely) the PERT approach factors in uncertainties to predict realistic deadlines.
As a result, PERT chart generator gives users a birds-eye view of the entire project before it's started to avoid potential bottlenecks.
Keep in mind: PERT charts are about big-picture planning. While they can be used during the project's implementation to track progress, PERT charts are not flexible enough for teams to adapt them to small changes when team members are confronted with roadblocks.
How to draw a PERT chart
You can design your PERT chart in a few different ways. The traditional PERT chart (also known as an activity-on-arrow diagram) contains two main elements:
- Nodes represent events or milestones in your project. You can use either numbered circles or numbered boxes.
- Arrows represent tasks—or the work necessary to reach project milestones. The direction of the arrows shows the sequence of tasks. Diverging arrows indicate that you can complete those tasks concurrently.
Follow these steps to put your PERT chart together:
- List all of the activities involved in the project.
- Consider dependencies.
- Place nodes and arrows based on the information you have gathered.
- Add completion time for each activity.
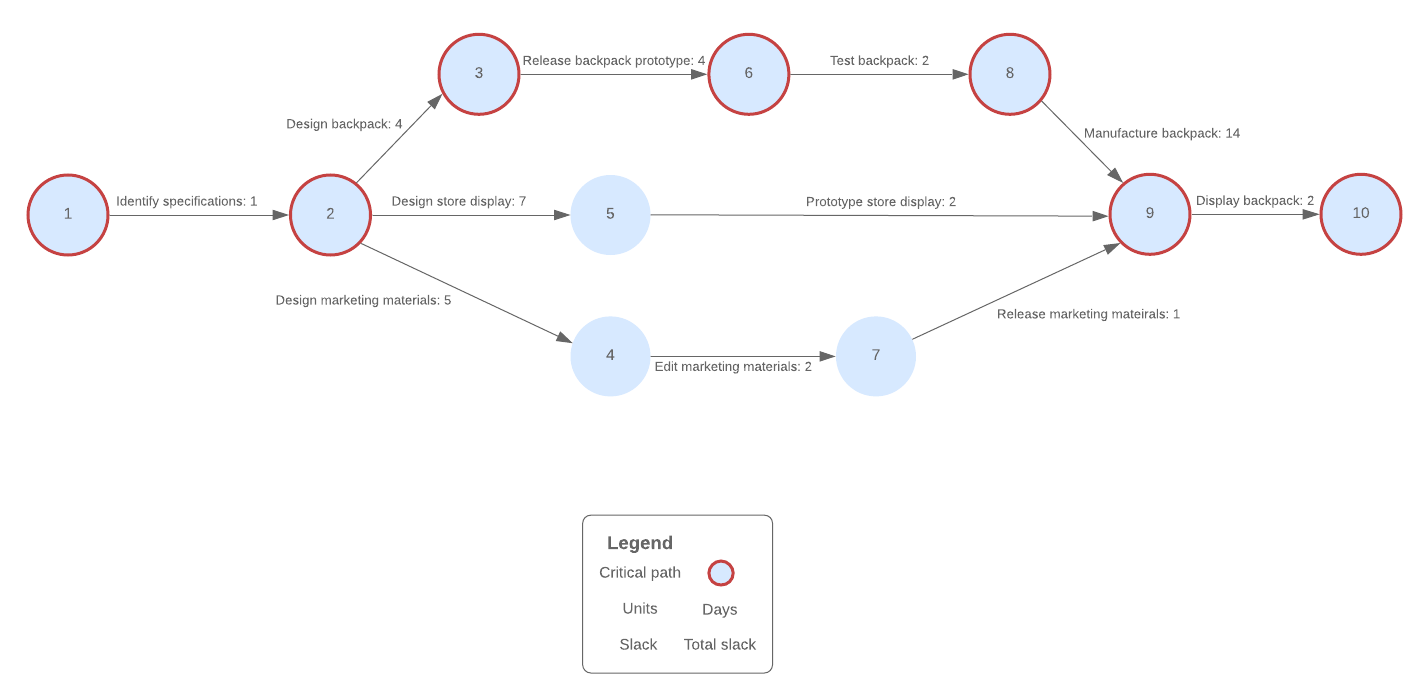
How to interpret your PERT chart
Once you draw your PERT chart, you'll want to use that information to determine a realistic timeframe for your project. This process is called the critical path method.
The critical path is the longest sequence of tasks that need to be done in order to finish the project. If any of these critical tasks are delayed, the entire project will be set back.
Find the longest path based on the time estimations you have entered. Remember that you’re not looking for the path with the most activities—you’re looking for the path with the activities that will take the longest. Add together the time it takes for each activity together and you’ll know how long the entire project should take.
Now refer to your PERT chart to ensure that you finish your project by the deadline or to adjust the times as circumstances change.

See a more detailed tutorial on how to create and use PERT charts for project management.
Learn moreWhat is a Gantt chart?
Created by Henry Gantt during WWI, Gantt charts visualize a project’s schedule from start to finish. Similar to a PERT chart, Gantt charts display tasks over time to ensure the project is completed on time.
Project managers use Gantt charts to identify task dependencies, increase efficiencies, and improve time management. Gantt charts make it simple to break down projects into manageable steps that can adjust to the project as needed.
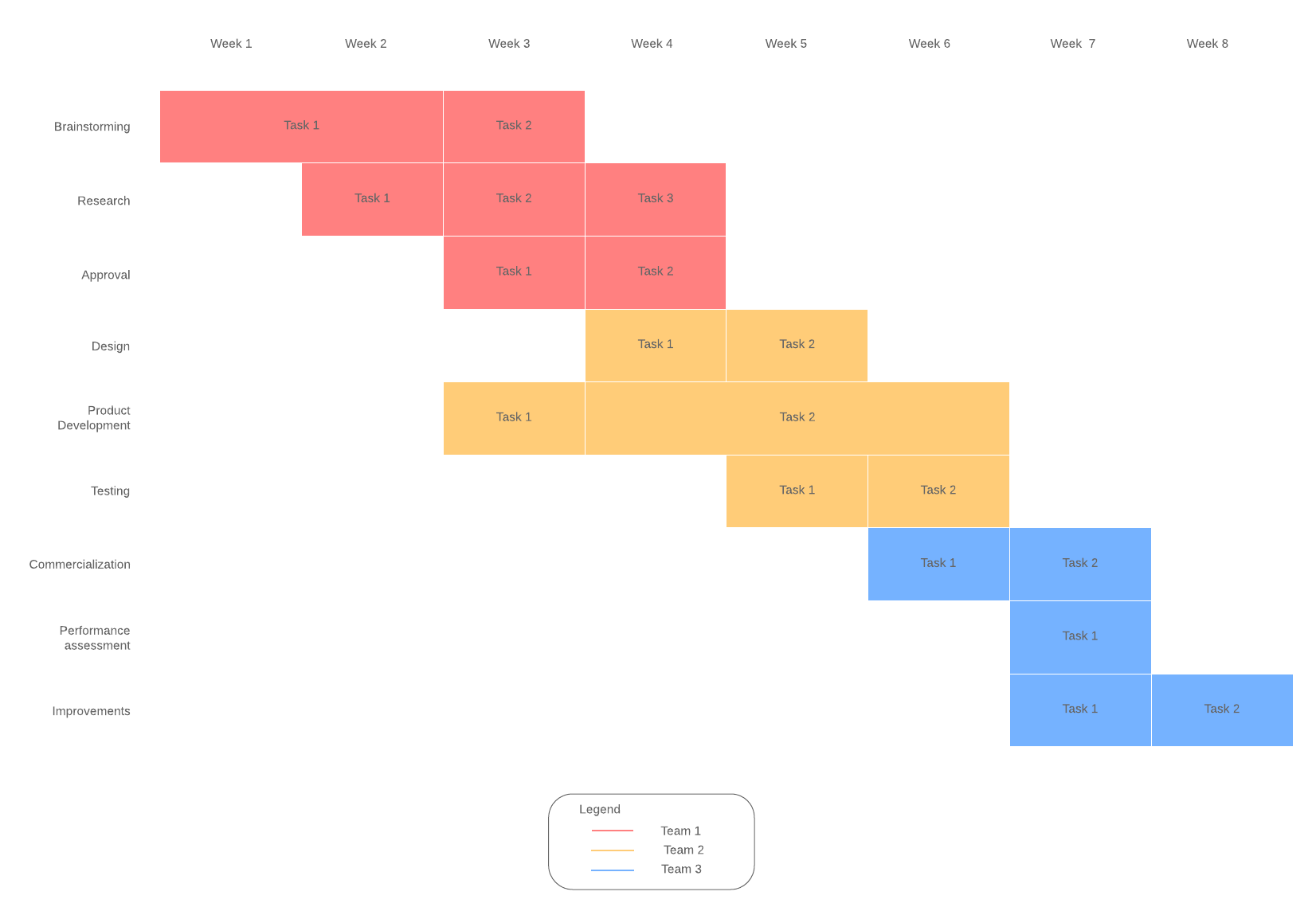
When project managers should use Gantt charts
Gantt charts are most useful to project managers during the project to make sure that each task is accomplished. Use Gantt charts to keep the project on track, communicate expectations and critical deadlines, and identify potential bottlenecks, resource overloads, or delays.
Keep in mind: While Gantt charts are valuable management tools, they also require a lot of upfront work and an accurate scope to be effective.

Find out more about using Gantt charts for project management.
Learn moreHow to build a Gantt chart
Gantt charts are visually similar to a bar graph. Tasks are displayed vertically, and the timeline runs horizontally along the top of the chart. Each task is represented by a horizontal block and the length of the block indicates how long a task will take.
Use the following steps to start your own Gantt chart.
- Determine tasks and subtasks.
- Identify task connections.
- Create a timeline.
- Order tasks.
- Use a template.
- Assign tasks.
- Chart progress.
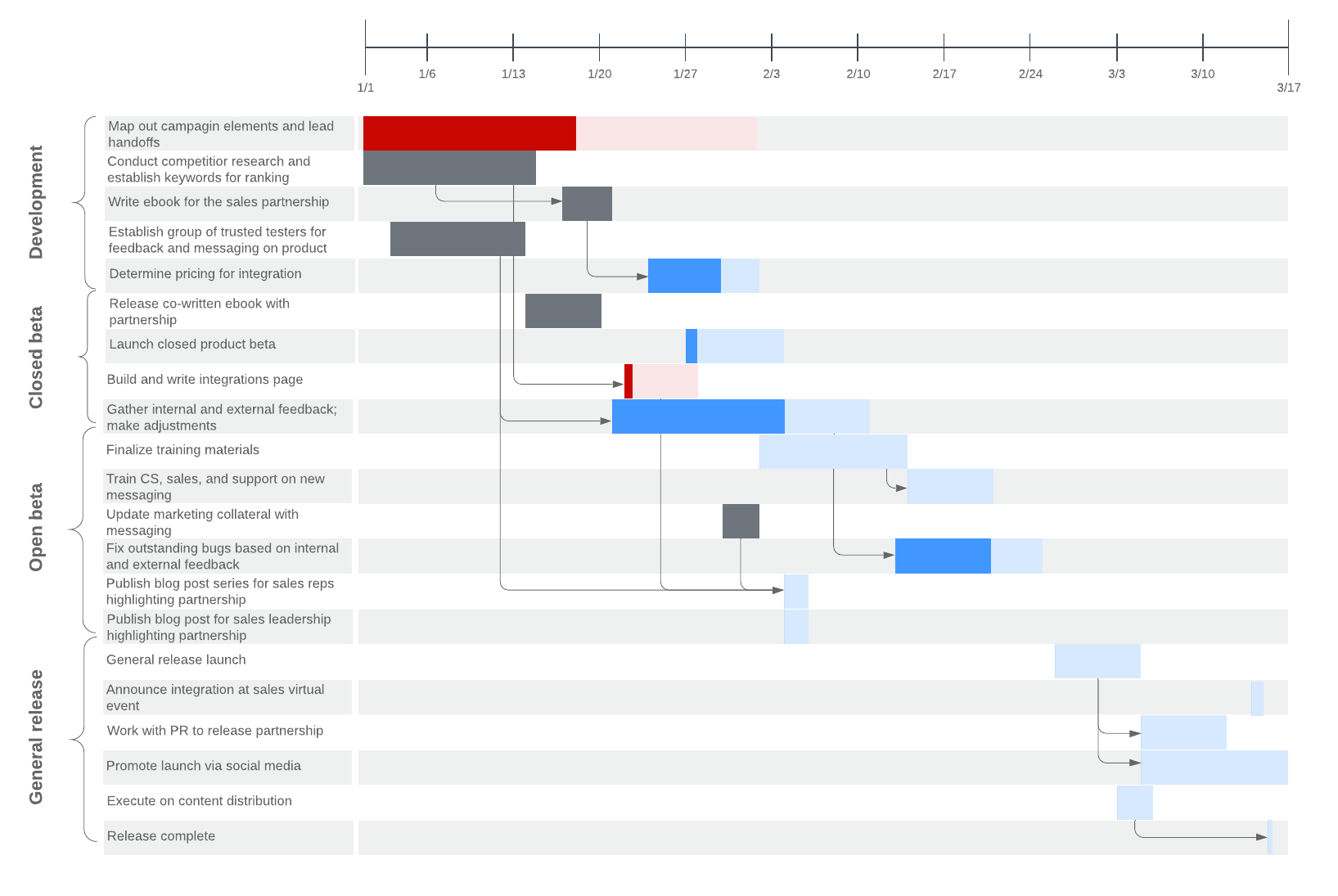
When to use a PERT chart vs. Gantt chart
Many people who ask “What is a PERT chart?” will immediately follow up with a second question: “How is it different from a Gantt chart?” Both are visual tools for project management, but you should consider some key differences between Gantt charts and PERT charts before you decide which will work better for your project.
Like PERT charts, Gantt charts break projects into smaller tasks and highlight scheduling constraints. However, project managers use Gantt charts while a project is happening—they schedule tasks by date and show how much work has been completed. Every activity is represented with a bar that stretches from the start date to the end date of that activity. Use a Gantt chart if you need to:
- Anticipate the amount of time to complete each task.
- Clearly communicate task responsibility.
- Increase transparency on the project's progress.
PERT charts are generally used before a project begins to plan and determine the duration of each task—so they don’t have to show the actual dates of your project. They also do a better job of showing whether certain tasks need to be completed in order or whether they can be completed simultaneously. Use a PERT chart if you need to:
- Show the interdependencies of certain tasks.
- Anticipate the amount of the time it'll take to complete a project.
- Determine the critical path to meet your deadlines.
- Plan for large or more complex projects.
Both PERT charts and Gantt charts simplify the project management process to increase efficiencies and see the entire project. Whether you decide to use a PERT chart to plan your project or a Gantt chart to track and manage progress, consider using both strategically to organize and implement your project.

Start your projects right and keep them moving forward—sign up for a free Lucidchart account.
Sign up freeAbout Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
Identifying and managing project constraints
This article discusses some of the constraints you might encounter and what you can do to work around them to keep your project on track.
How to Make a Gantt Chart in Excel
Learn two approaches on how to make a Gantt chart in Excel with this complete step-by-step guide. Free templates included!
Advantages of PERT charts vs. Gantt charts
What's the difference between a PERT chart and a Gantt chart? Both of these tools can improve your project management processes. Learn when to use PERT and Gantt charts and how to create them.
How to use a Gantt chart
Gantt charts visualize an entire project from start to finish, making it easy to track progress, improve efficiency, and clearly communicate with the project team.
