So you’ve chosen Lean manufacturing as your process improvement methodology. But knowing about Lean manufacturing and knowing how to implement it are two very different things.
We’re here to help. This article will guide you through implementation with the top Lean manufacturing tools you’ll need to get going. (Side note: These tools are also applicable to Lean Six Sigma.)
Implement these tools and stay focused on the real customer-driven benefits of Lean manufacturing. That way, even though Lean production may be difficult at the beginning, you'll be able to keep going and develop processes that continuously improve over time.
What is Lean manufacturing?
In the simplest terms, Lean manufacturing focuses on constantly improving customer value while minimizing waste. Instead of encouraging management to think of maximizing separate verticals, Lean optimizes the flow of production through value streams that touch every technology, asset, and department.
As you can imagine, changing the mindset of an entire company takes time, so implementing the Lean process may be a slow shift. But trust us, it’s worth it.
5 main Lean management principles
There are five principles that are the guiding stars of the Lean management process. Each tool you implement will bolster the implementation of these principles.
- Identify value: Value includes everything that benefits the customer. You’ll need to distinguish value-adding benefits from wasteful processes.
- Map the value stream: Once you know what value the product brings to your customer, you’ll need to track its path through production to consumer.
- Create flow: A smooth flow has eliminated bottlenecks and waste from production processes.
- Establish pull: When your team has time and bandwidth, they can start new work. In a pull system, the team only begins a task when they have the capacity to complete it.
- Continuously improve: Your customer’s perception of value will change over time, so your process must be constantly evolving to generate more and more value.
Keep reading for valuable tools that will improve your process and help you implement Lean production methods.
Best Lean process improvement tools by task
There are a ton of process improvement tools you should consider when you start using Lean manufacturing, so we’ve broken them up into each stage of the Lean process. When you find a tool that fits your needs, click the corresponding template to start editing and collaborating in real time within Lucidchart.
While a few of these tools originated with other process methodologies you can still apply them to help your company execute the Lean manufacturing process.
To define and prioritize
In order to identify value, you’ll need to analyze your value stream and find where waste is located. You’ll also need to establish how value travels on its path to the customer so you can make that path more efficient. Use these Lean tools to help:
Affinity diagram
Great for the initial stages of Lean implementation, affinity diagrams help sort large amounts of data or ideas. In this context, they can help you identify customer value and gather problems with current processes.
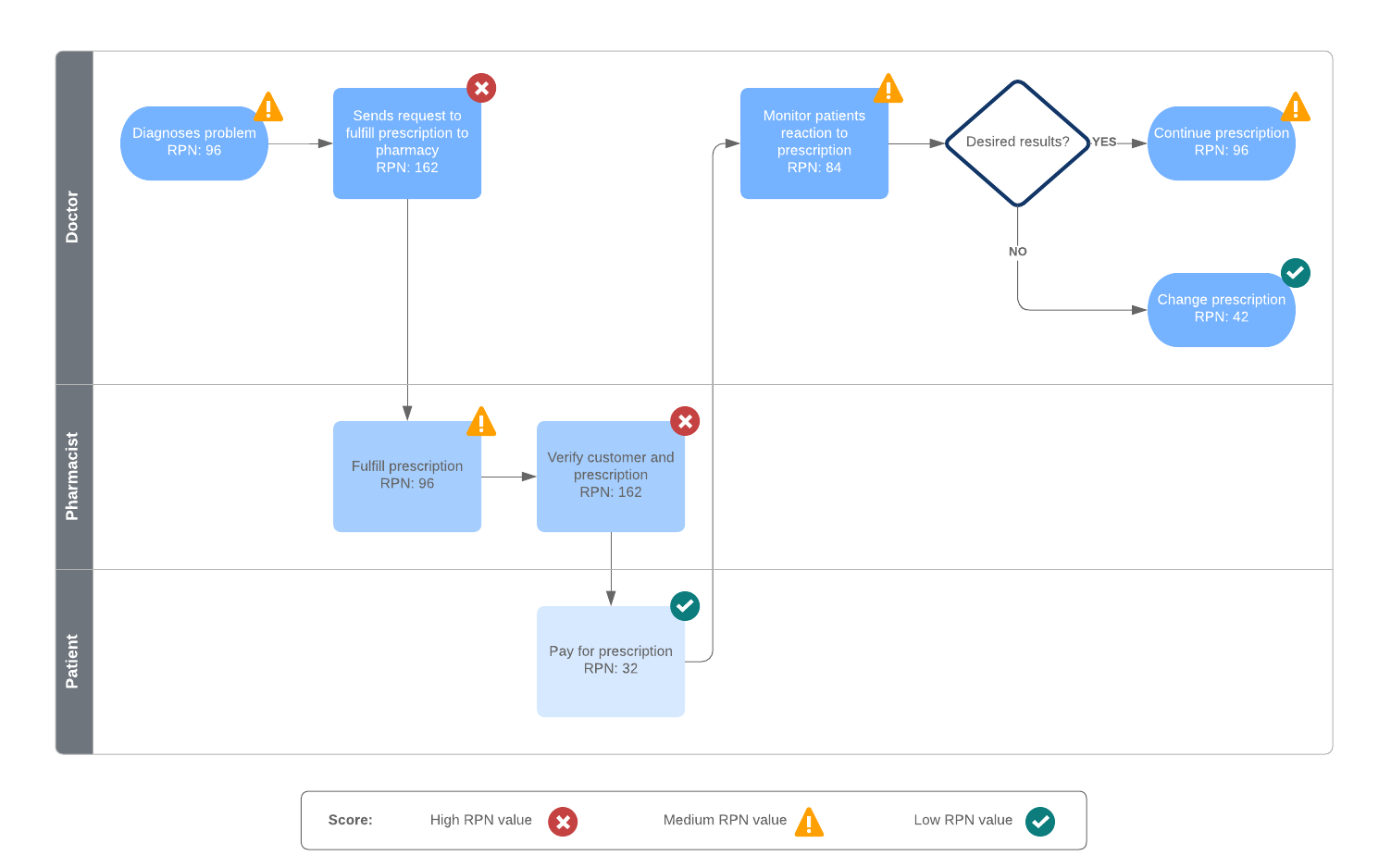
Failure mode and effects (FMEA) analysis
To eliminate waste as part of Lean manufacturing, you need to understand what could go wrong in your processes. FMEA analysis allows you to review your flow and anticipate and address issues before they become severe.
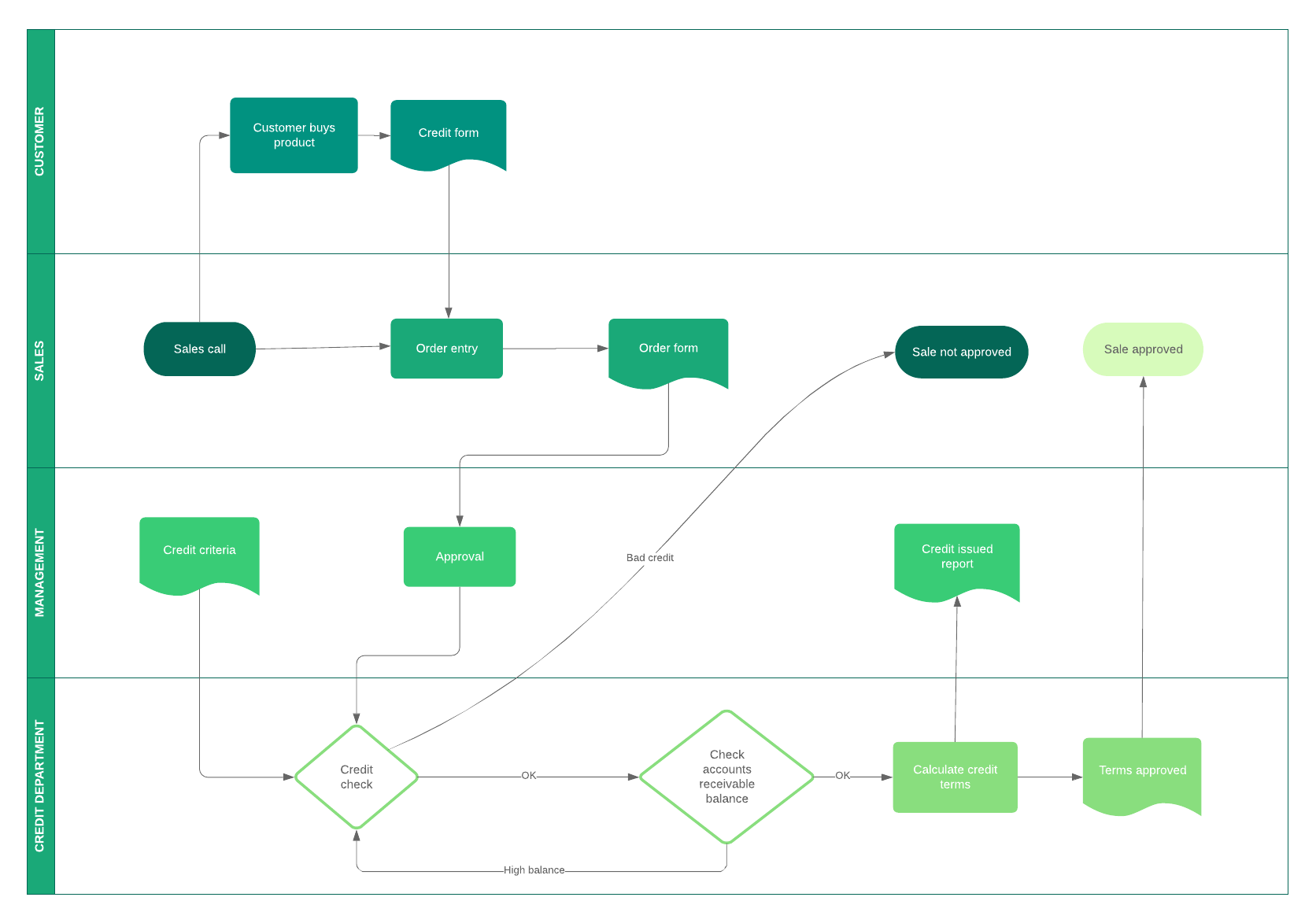
Value stream analysis
A value stream is everything your organization does to produce and deliver your product or service to your customers. Once you understand how your value is ultimately delivered to the customer, you can work on perfecting the process of delivery. Create a value stream map to analyze where you can cut non-value added activities.
Process flowcharts
The easiest way to create and maximize flow is to visualize it. Process flowcharts can help you track flow in an easy-to-understand way.
To analyze root causes
If a key goal of Lean manufacturing is to remove waste from your workflows, you’ll need to first identify the root cause of that waste. Get started with these two tools:
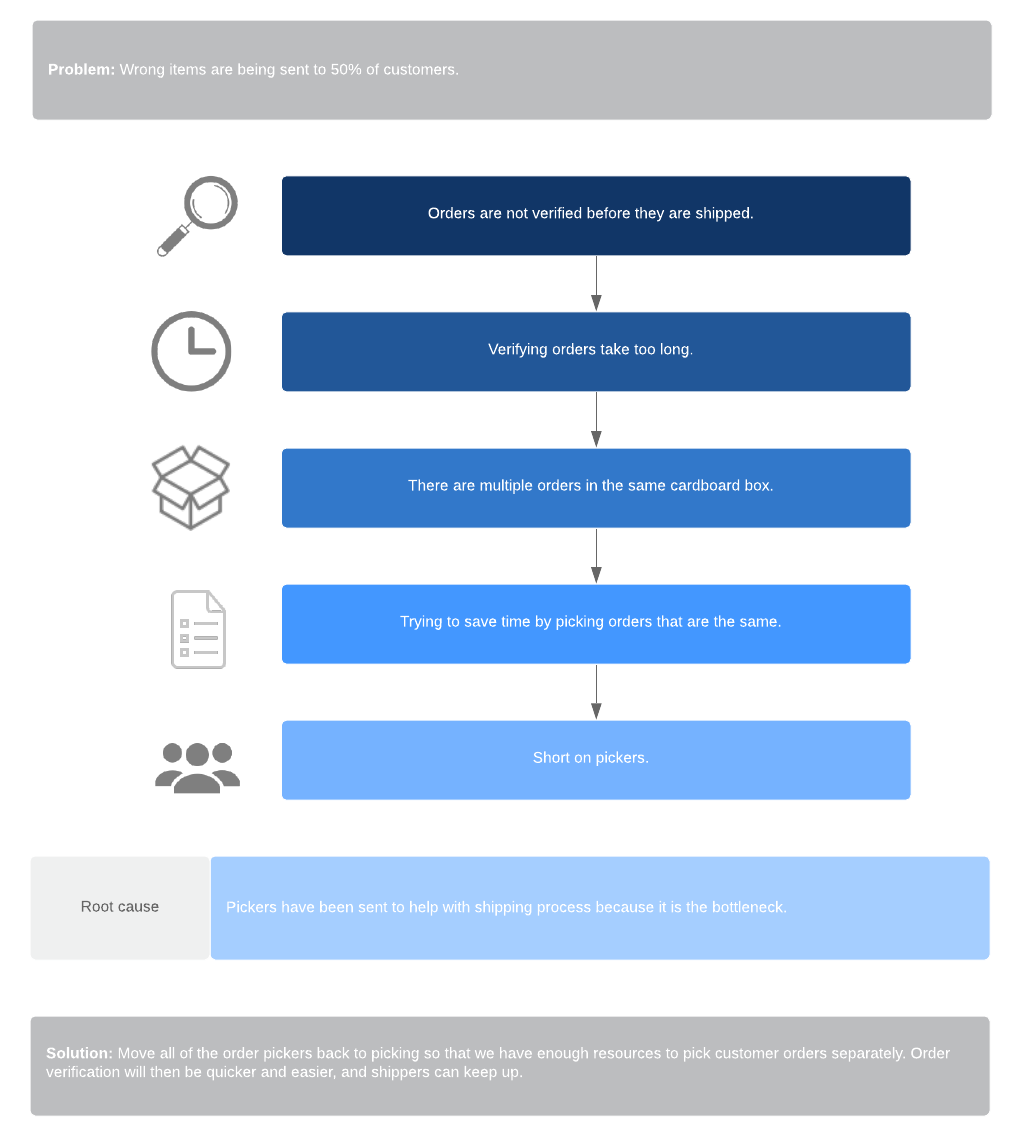
5 why analysis
To understand issues in the process, you may need to implement a 5 why analysis, a process where you keep asking “Why?” until you eventually reach the root cause. This template will help you and your team think critically to identify solutions to even the largest problems.
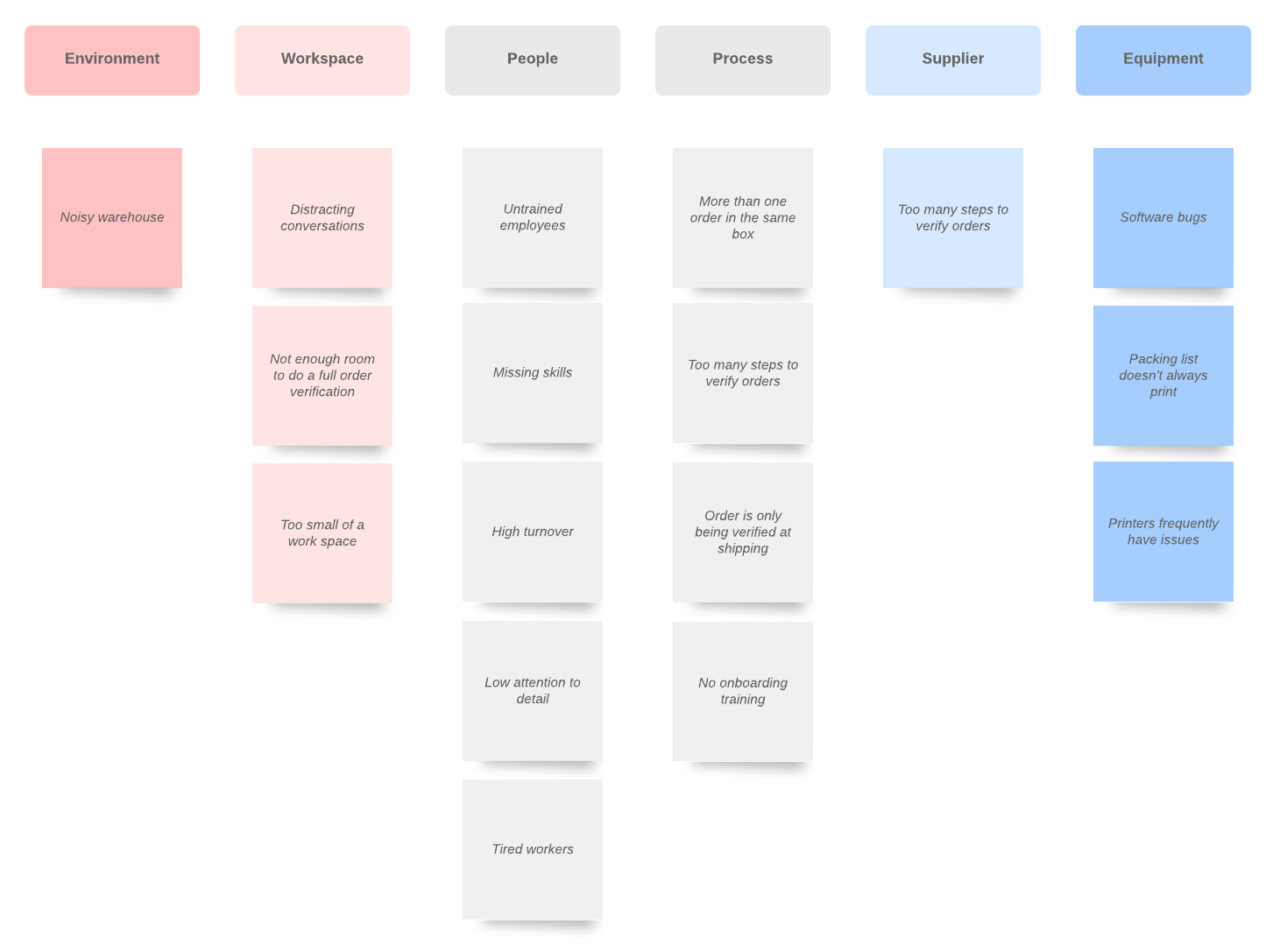
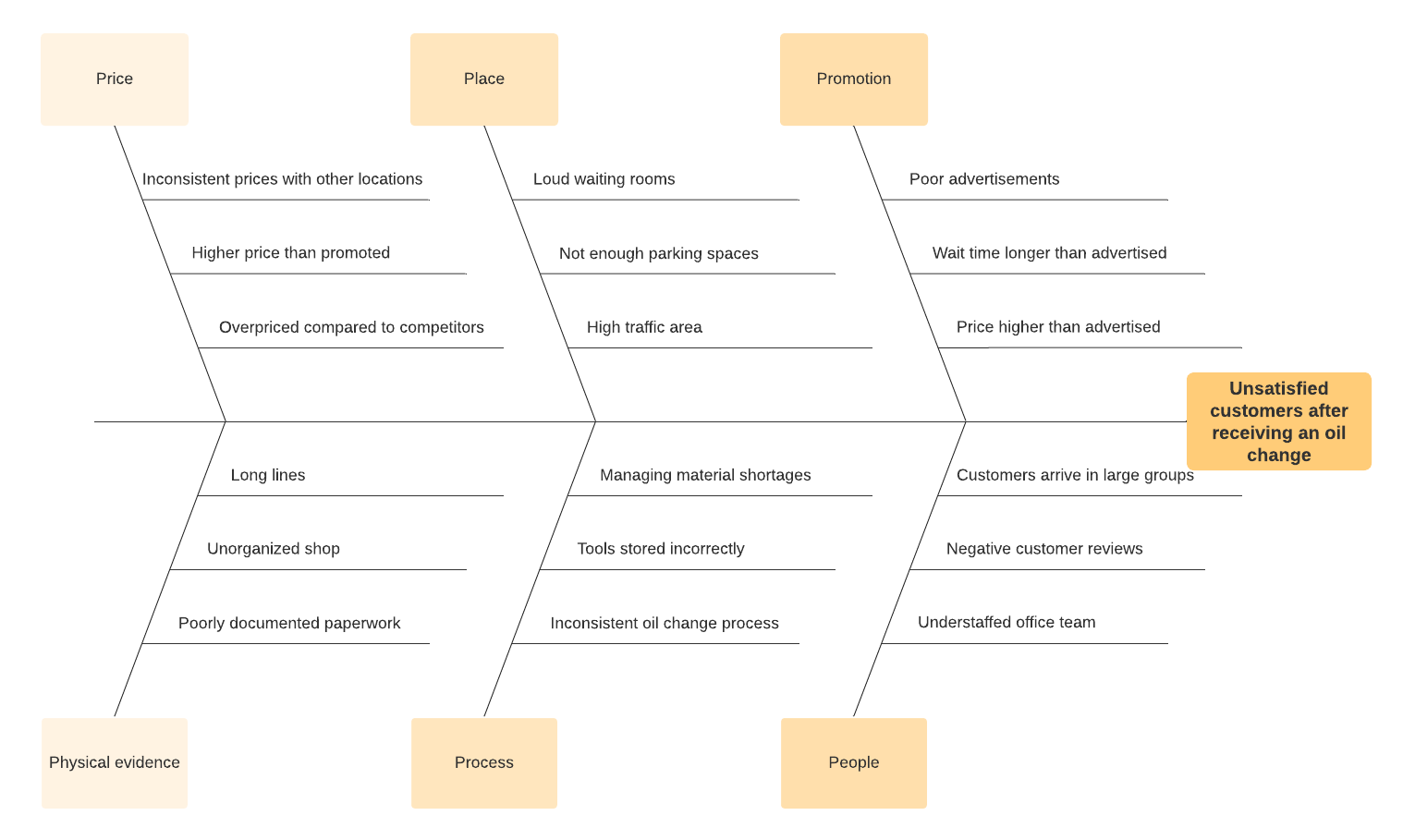
Fishbone diagram
Also known as a cause-and-effect diagram or Ishikawa diagram, the fishbone diagram can help you effectively eliminate issues by examining a problem from multiple angles. In a typical fishbone diagram, you would consider these categories of potential causes: measurements, materials, people, machines, methods, and environment. But you can adapt this diagram to fit your organization.
To implement improvements
Once you understand your process and have identified issues that are causing waste, it’s time to implement improvements. But implementation can often be the most difficult part of the Lean or Lean Six Sigma process. Use these diagrams to help:
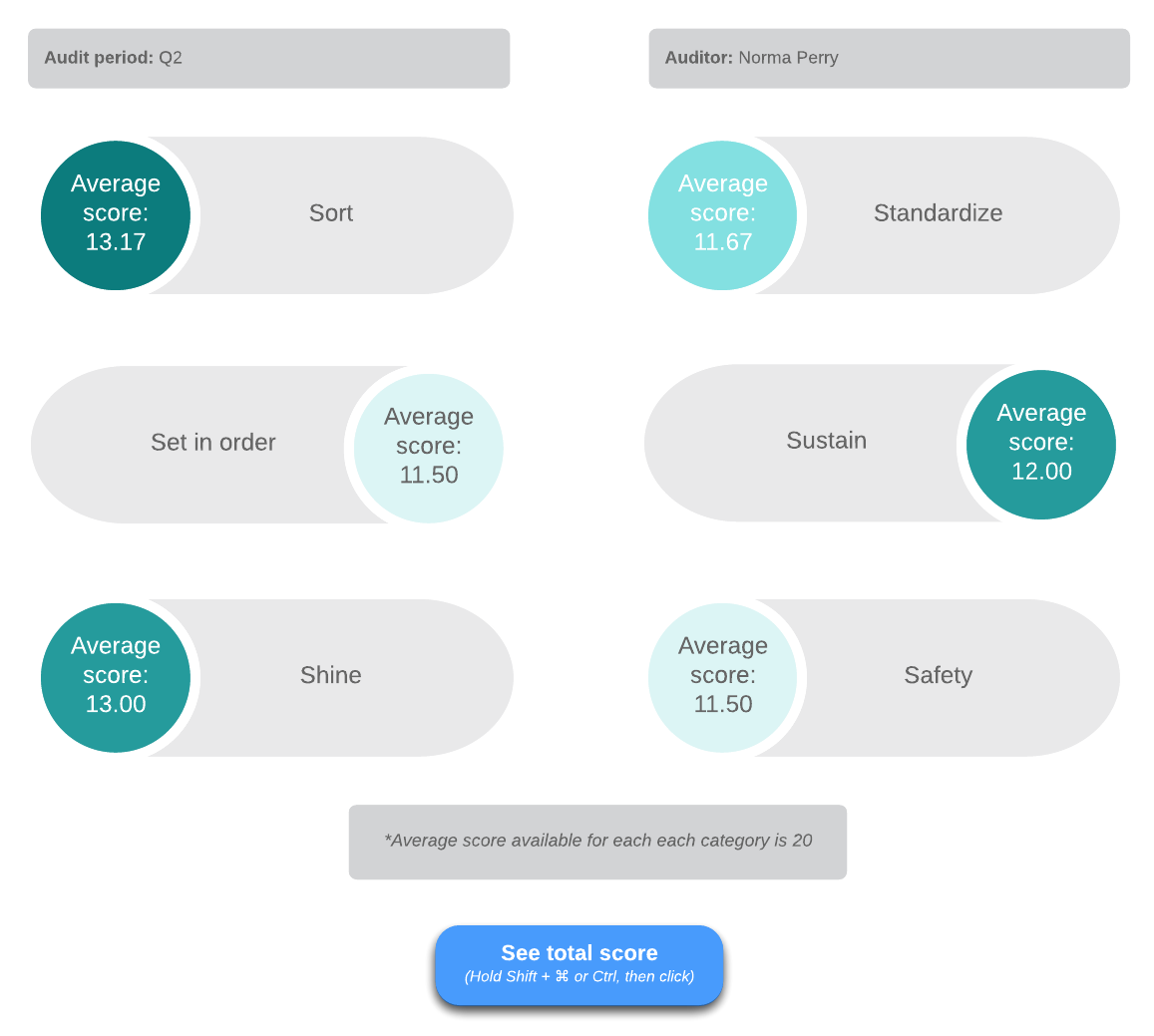
5S dashboard
Often used in manufacturing, the 5S approach will help you organize your workspace for maximum efficiency. Based on five Japanese terms, the 5 S’s translate to:
- Sort (remove unnecessary items from the location)
- Set in order (put items in the best place for their function)
- Shine (clean and inspect the workspace regularly)
- Standardize (create repeatable processes to implement the first three practices)
- Sustain (train workers and perform audits to ensure processes are followed)
Some organizations have added a sixth practice—safety—to identify hazards and set controls to ensure workers are safe. A dashboard can help you track how employees are performing in each of these areas.
Error-proofing
Create a flow that is designed to be fail-proof. Commonly known by the Japanese term poka-yoke, this tool involves implementing mechanisms that keep your company from producing products with defects, thereby avoiding waste. There are three main types of error-proofing: warnings (think of a fire alarm), shutdown controls, and autocorrection controls.
A3 report
An A3 report includes the most essential information about your processes to present progress, eliminate waste, problem-solve, and make better decisions.

Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
The TPM method gets machine operators involved with regular preventative maintenance to ensure equipment reliability, increase productivity, increase capacity, and improve quality.
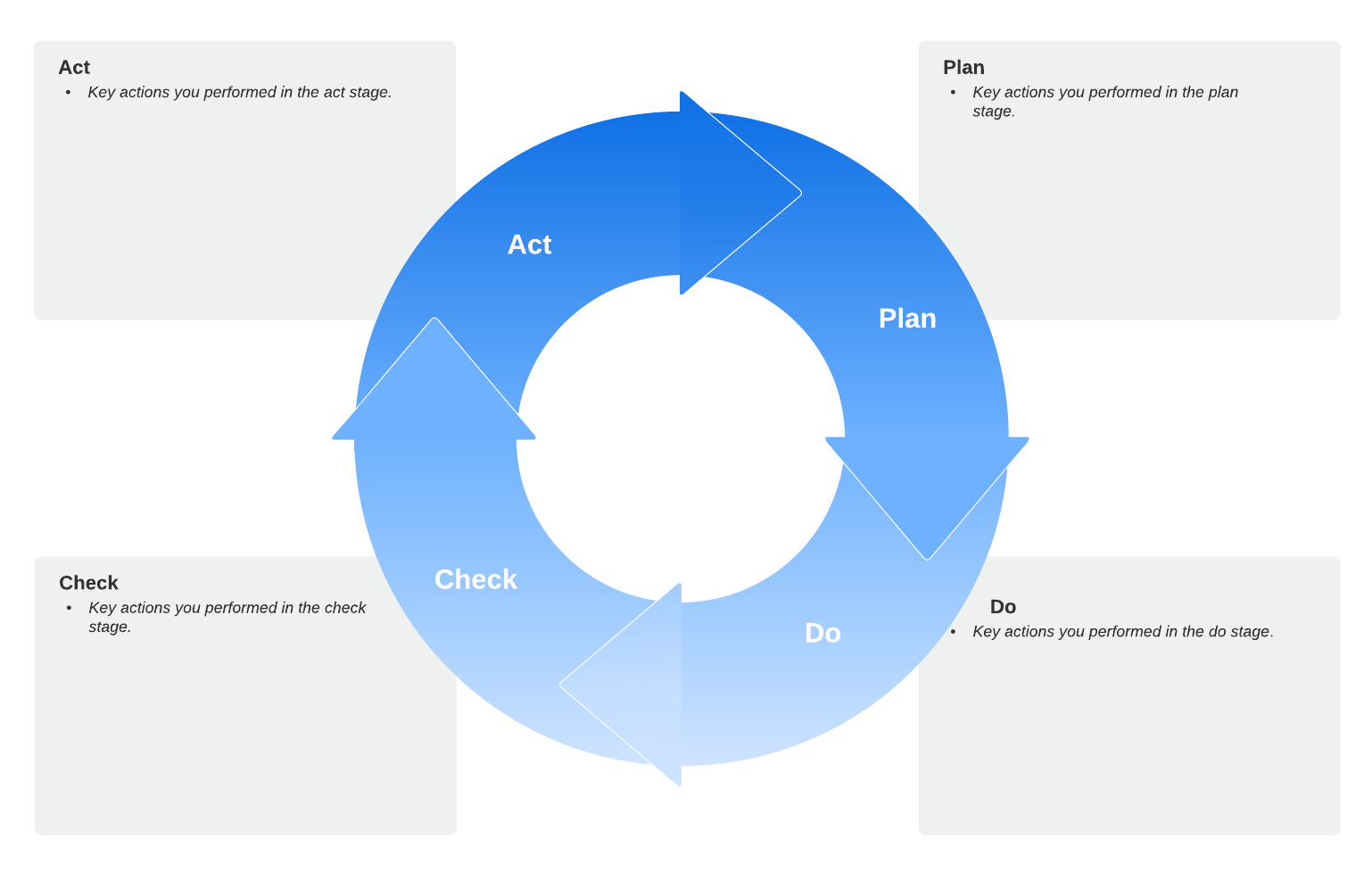
Plan Do Check Act (PDCA) cycle
The PDCA cycle is a key element of Lean management—this tool helps companies transition to continuous improvement. Professionals using this repeatable method will analyze a problem or an opportunity to change, test a hypothesis, review and analyze the results, and implement the plan if successful.
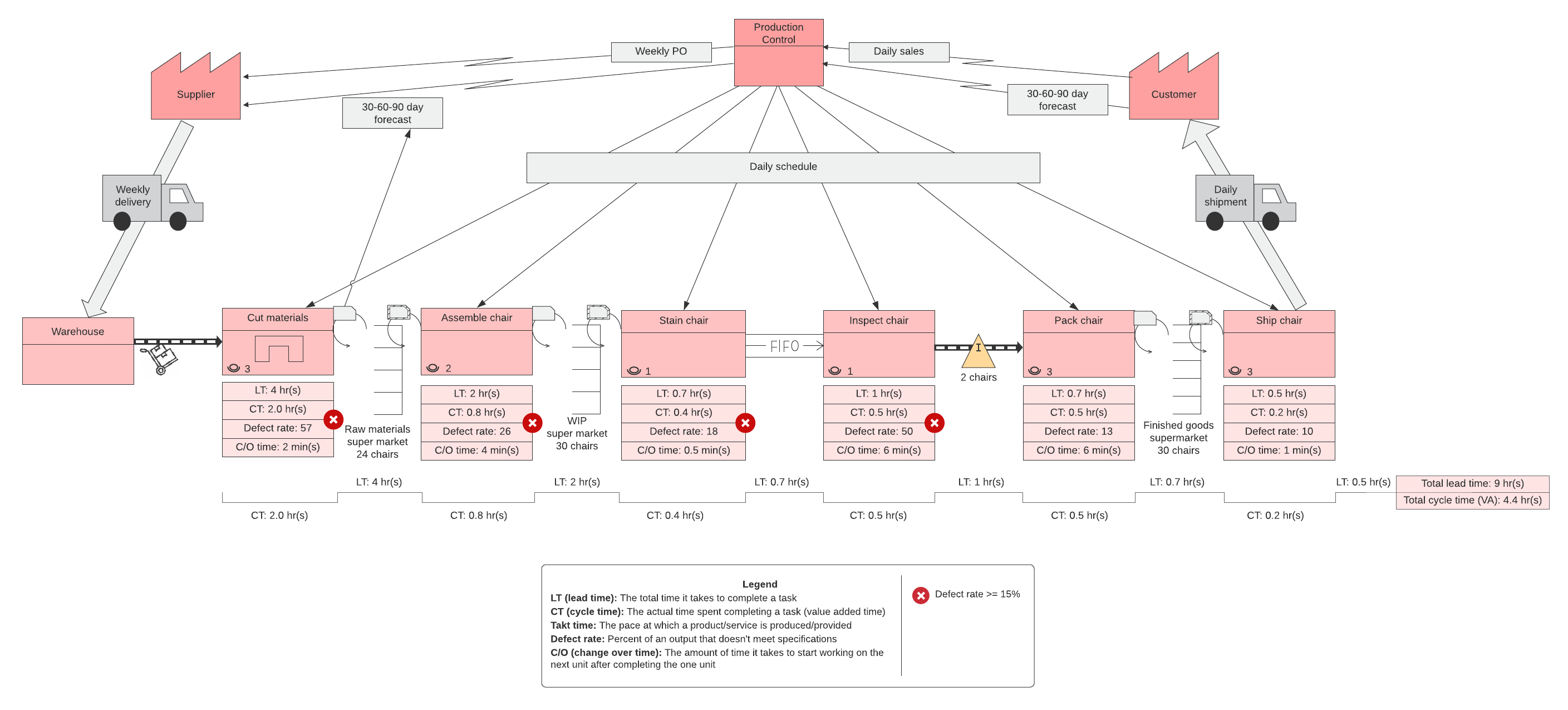
Value stream map
A value stream map visualizes the steps involved with delivering a product or service. Within your value stream map, you’ll track important data to see where waste exists and whether you’re delivering the quality your customers expect. This data can include takt time, or the maximum amount of time you can spend to satisfy customer demand.
Control the process
Arguably the most beneficial aspect of the Lean manufacturing process is its focus on continuous improvement. This mindset allows organizations to evolve along with customer needs and to continuously adapt to the changing world. Apply these diagrams to control processes and focus on improvement.
Cellular manufacturing
Also included within just-in-time manufacturing, cellular manufacturing eliminates waste using an assembly line method. A product moves from one “cell,” or a machine that accomplishes a specific task, to another cell.
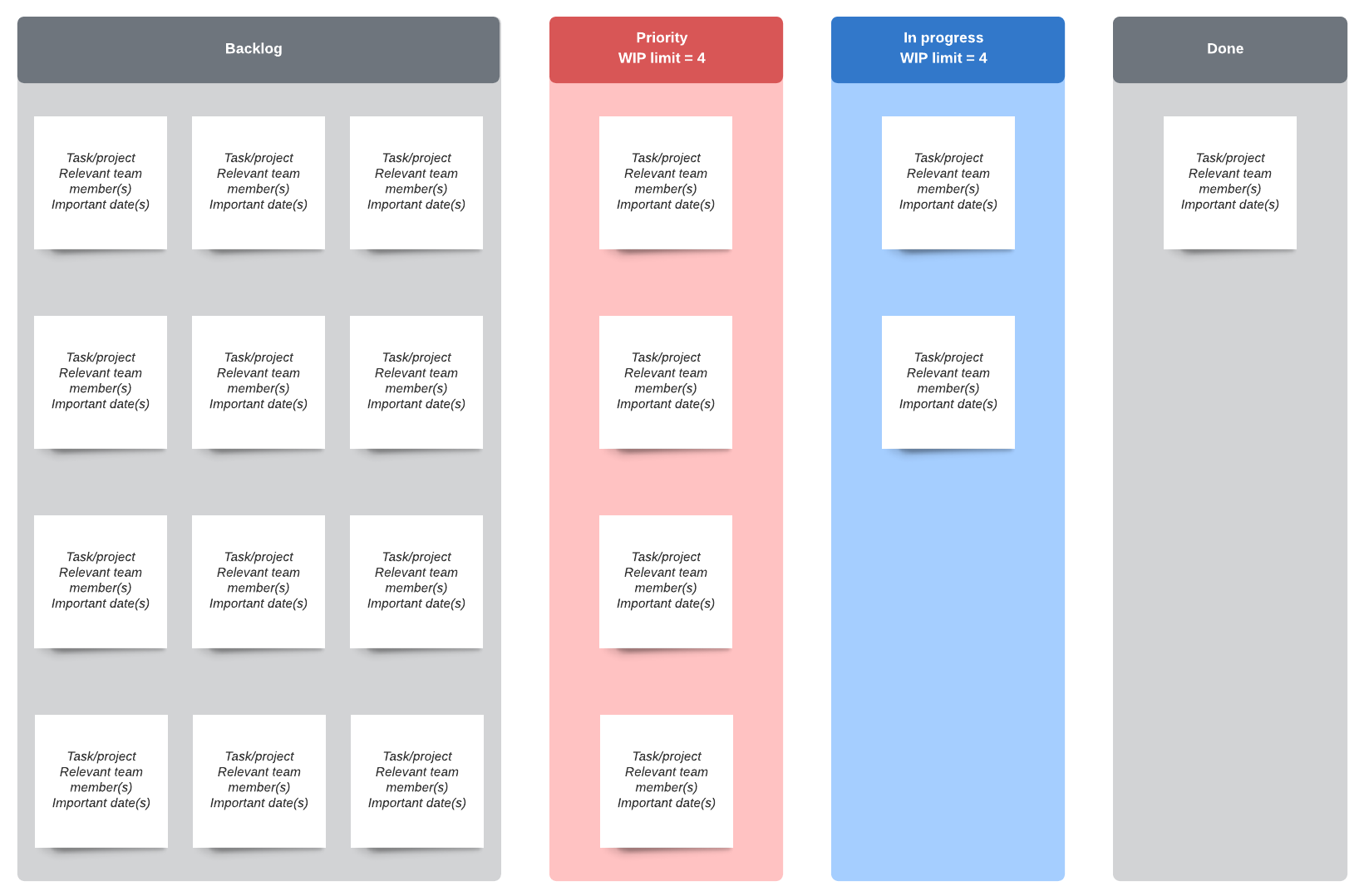
Kanban
Although many think of Kanban boards for project management, Kanban can also be a means to control production: which items are produced, how many, and when. With the Kanban method, a pull queue can be set up ahead of time, and tasks can be “pulled” from the list as needed.
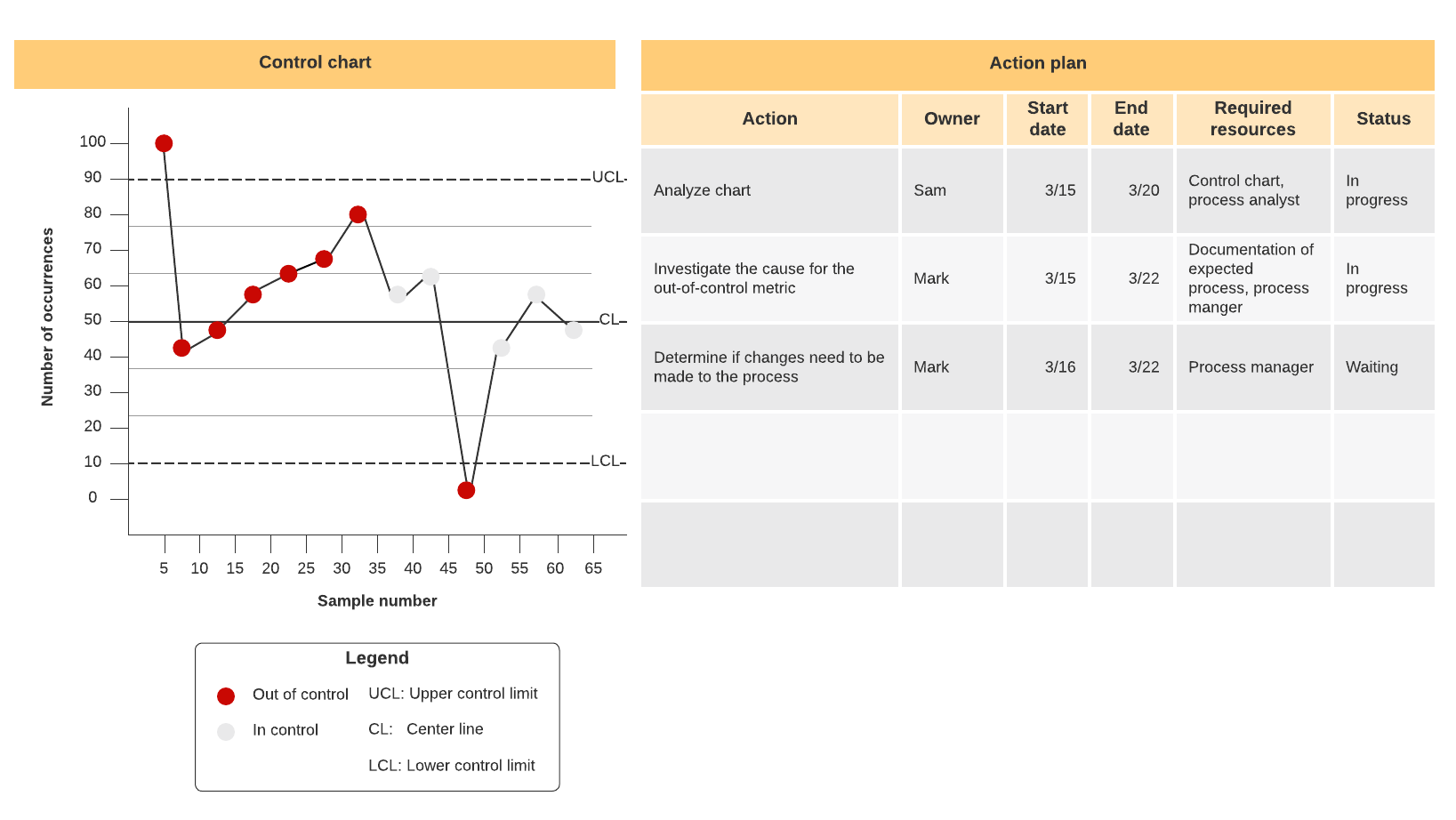
Control plan
This tool will help you track each step of your process and take corrective actions for continuous improvement.
Developing your strategy
Each organization is different, so you may need to experiment to discover the templates and diagrams most appropriate for your company. You’ll find, however, that even the most basic tools can really hone in your organization’s ability to eliminate waste and focus on continuous improvement.
It may seem like too great a task for a flowchart or diagram, but you’ll be surprised at the impact these seemingly small tools have on your implementation of Lean manufacturing techniques.
Now that you know which Lean tools to use, learn how to standardize your business processes with Lean manufacturing.
Learn moreAbout Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
Single-Minute Exchange of Dies: Improving lean operations
Keep reading to discover what SMED is, why it is beneficial, and how to use the SMED process to improve operations within your organization.
Lean methodology 101
In this article, we’ll discuss how the Lean methodology can help you to improve productivity, eliminate waste, and keep your customers happy.
Lean vs. Six Sigma: Determining the Right Method for Your Business
Six Sigma and Lean are process improvement methodologies that will help your company eliminate defects and waste to improve quality and efficiency. Read on to determine the right approach for your business.
Everything about 5S in Lean manufacturing
A handy overview of the 5S methodology and how you can use it to improve your Lean manufacturing process.

