For your business to grow, you must embrace change. Yet, only 34% of change initiatives succeed. So you need to make sure that the proposed change makes sense, will help you achieve your goals, and will be embraced by all employees.
One of the ways to do that is by following a strategic change management framework like the 7S model by McKinsey.
Developed in the late ’70s by McKinsey consults Thomas J. Peters and Robert H. Waterman, the McKinsey 7S model is a framework that helps you assess seven key elements of your business's organizational design that need to change or be aligned in order to be successful.
In this article, we will discuss the McKinsey 7S framework and show how to use this model. We will also give you ideas about how to make the McKinsey 7S model accessible to everybody involved for effective collaboration.
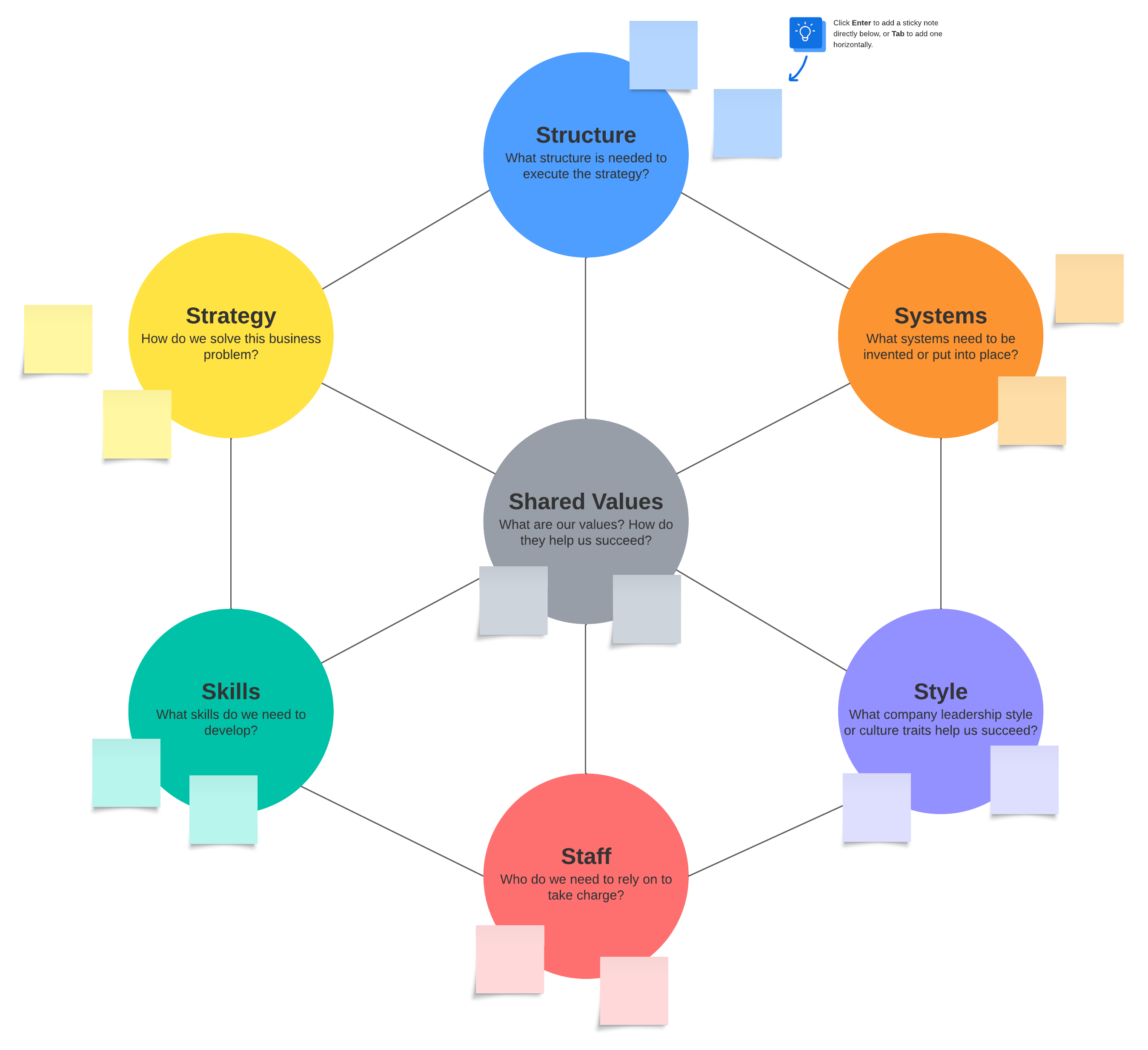
7 elements of the McKinsey 7S model
The basic premise of 7S management is that there are seven interconnected elements of an organization that need to be aligned so it can be successful. When one element changes, it impacts the other elements. These seven elements are categorized as “hard” or “soft.”
Hard elements
The hard elements are tangible, easy to identify, and easier for management to immediately influence, such as strategy statements, corporate plans, organizational charts, and other documents.
- Strategy: your company’s plan to enhance competitive advantage
- Structure: how your company is organized and who reports to whom
- Systems: procedures, processes, and routines of staff that characterize how the job is done
Soft elements
These elements are more difficult to describe because staff capabilities, corporate values, and culture are continuously developing and changing.
- Shared values: the core values that are reflected in the corporate culture and individual work ethic
- Style: typical behavior patterns of groups such as managers and other professionals
- Staff: your company’s employees and their general capabilities
- Skills: the organization’s core competencies and distinctive capabilities
The 7S model diagram represents the interdependency of all seven elements. Shared values are placed in the middle of the model to emphasize that they are central to the development of all the other critical elements. The ideas behind why the organization was created will influence the other six elements.
Use a Lucidchart template to create a web-based McKinsey 7S management model that you can use to collaborate with others as you realign goals and work through organizational changes.
How do you use the McKinsey 7S model?
The interdependency of this strategy development framework means that if one element changes, you will have to address the other six elements to analyze how the change affects them and to determine how each may need to change to keep organizational goals aligned.
Business uses of the McKinsey 7S framework include:
- Determining how your business will achieve targets and goals
- Boosting productivity and performance
- Putting a proposed strategy into effect
- Facilitating the complexities of aligning departments and processes during mergers or acquisitions
- Examining the effects of organizational changes within the company
- Implementing policies to improve employee skills and competency
The McKinsey 7S model can be used when organizational design and effectiveness are in question. It can help all stakeholders to work towards agreement when there are differing opinions about how the seven elements should be aligned.
The following steps should help you as you implement this tool.
Step 1: Identify areas that need to be aligned
Analyze each of the seven elements to determine if they are effectively aligned with the others. For example, if you designed a strategy that relies on quick product introduction, but you use a matrix structure with conflicting relationships that hinders an agile work environment, there’s a conflict that requires a change in strategy or structure.
To perform a 7S analysis, answer these questions:
Strategy
- What is your company’s goal?
- How will resources be used to accomplish that goal?
- What is unique about your company?
- How do you adapt to changing market conditions?
Structure
- How is the company organized?
- How are decisions made?
- How do employees align themselves to the company strategy?
- How is information shared?
Systems
- What financial systems are in place for resource acquisition?
- What systems are in place for recruiting, promotion, and performance appraisal?
- What processes, procedures, and routines are in place to get work done?
Shared values
- What are the values upon which the organization was built?
- How do the values play out in daily life?
Style
- What is the leadership style?
- How do employees respond to management?
- Do employees function competitively, collaboratively, or cooperatively?
- Are there teams or silos?
Staff
- Is the current number of employees enough to accomplish goals?
- Are there staffing needs?
- Are there gaps in required capabilities or resources?
Skills
- What skills do employees have to deliver core products and services?
- Are the current skills of your employees sufficient?
- What does the organization do well?
- How are skills monitored, assessed, and improved?
After you have answered these questions, analyze the data and look for alignment, consistency, conflicts, gaps, strengths, and weaknesses.
Step 2: Determine your optimal organizational design
When you can determine the organizational design that is most effective for you, it makes it much easier to set goals and make action plans. To help you find your optimal design, look at your competition and other departments within your company to see what is working for them.
Use Lucidchart to create documents that can help you hone in on the design that will most efficient for you. Lucidchart documents are web-based and can be accessed from anywhere at any time, allowing for true cross-team collaboration.
Step 3: Decide what needs to change
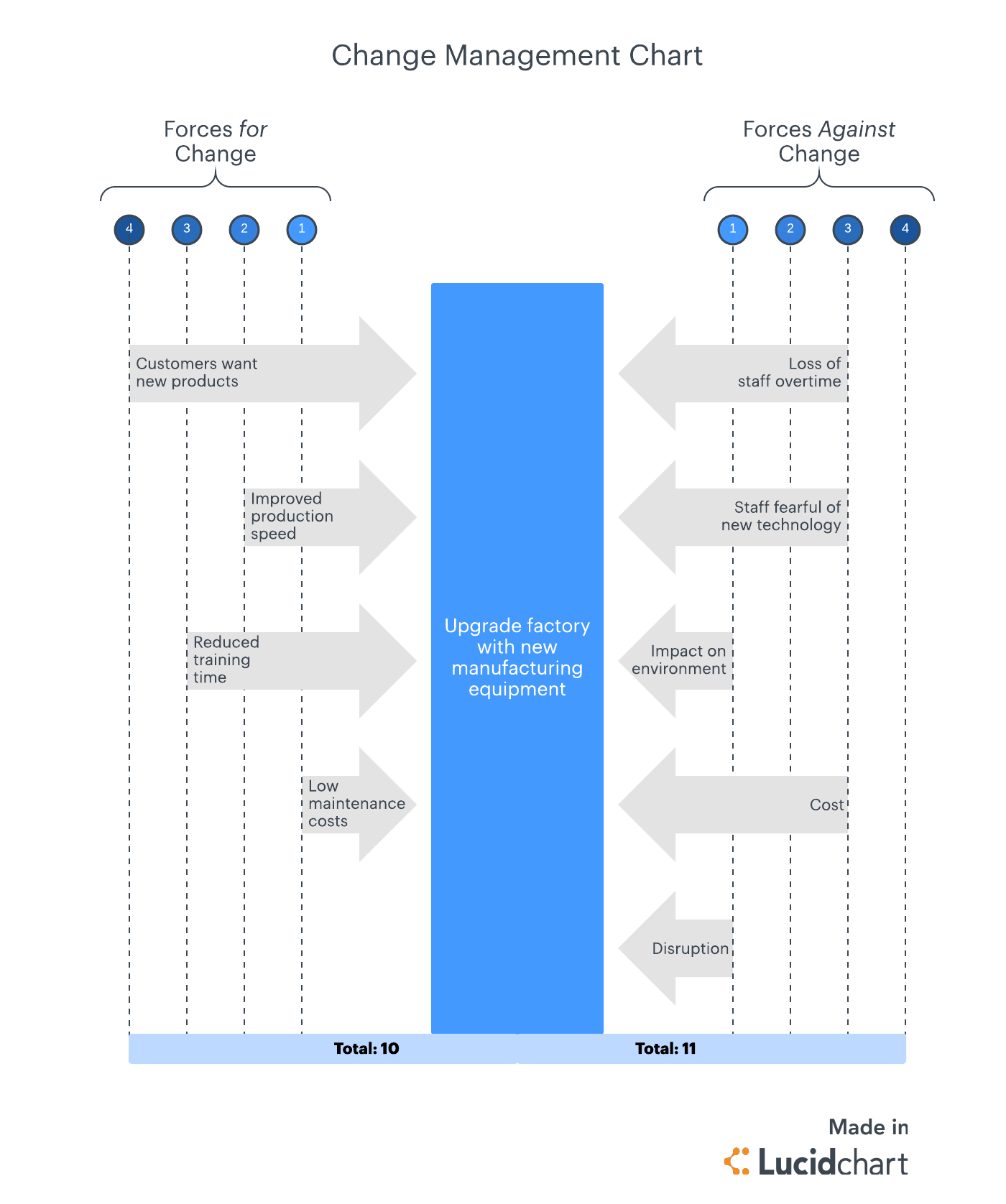
Create an action plan that details the areas that need to be realigned and the steps you need to take to achieve those realignments. For example, if the management style of some of your leaders does not align with your company’s values, you’ll need to decide what changes need to be made: Will you need to remove a layer of management, reorganize reporting hierarchies, or simply influence managers to change their style so operations will work more efficiently?
Using data you have collected from previous organizational changes and from analyzing how your competitors have successfully implemented change in the past, build a flowchart to visually outline your change process. Your flowchart should include a representation of procedures and processes as they are now and how you want them to change in the future.
An easily accessible flowchart lets you and your team analyze strengths and weaknesses and collaborate as you propose future changes. By supporting real-time collaboration, Lucidchart allows for greater buy-in from employees and leadership.
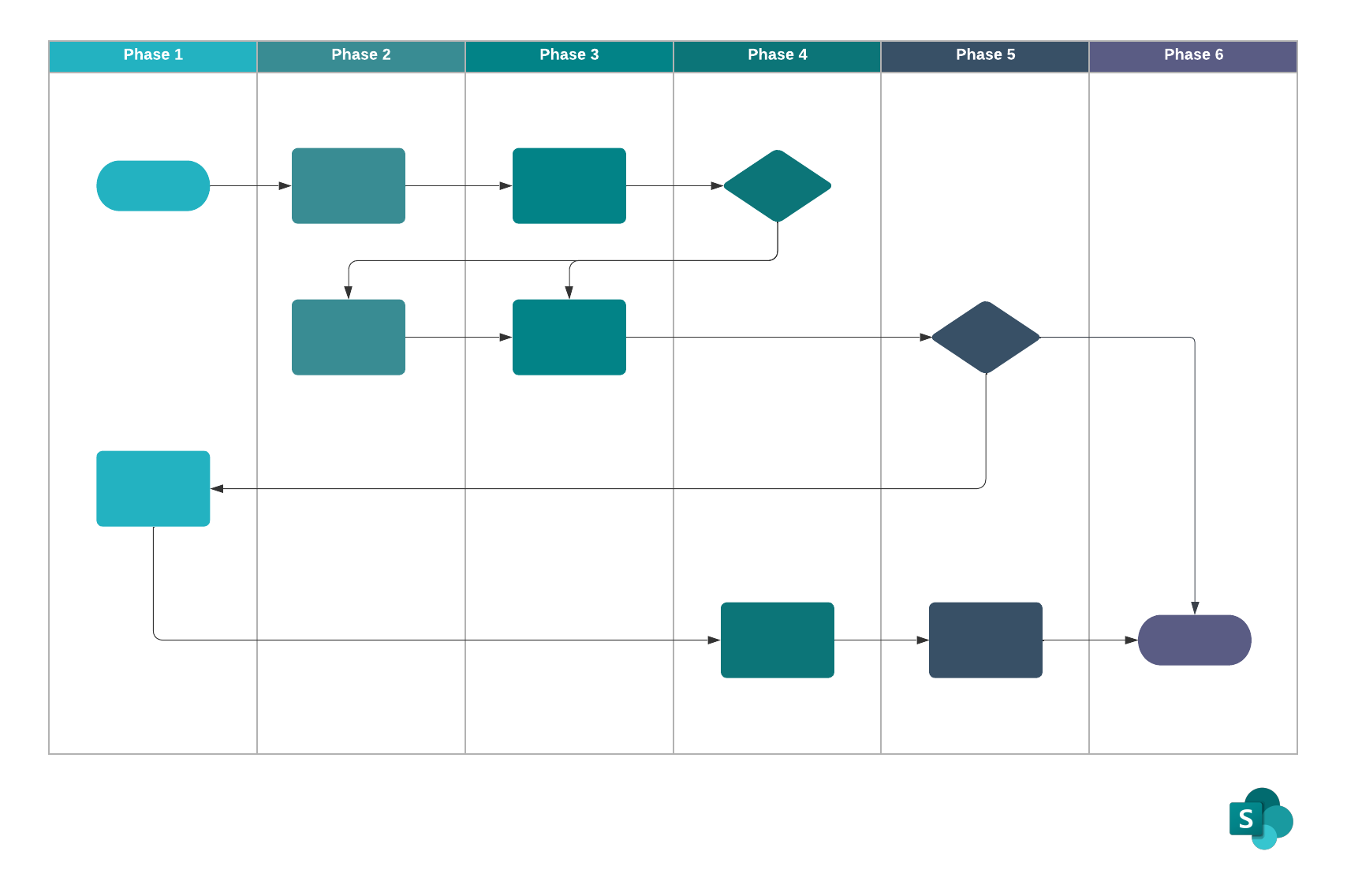
Step 4: Implement the changes
After you have decided on the changes that need to be made and have complete buy-in from everybody involved, you’ll need to implement the changes. Only changes that are implemented correctly will have a positive impact on your business. Find people in your organization or bring in consultants who have experience in implementing changes smoothly.
When there are a lot of changes that need to be made, consider implementing them in phases so that the organization is not overwhelmed. To do this, you should use Lucidchart to visually map out an implementation plan.
Step 5: Review the seven elements in your strategy development framework
The McKinsey 7S model is dynamic and should change often as you look for ways to be more efficient and grow your business. Return to the model often to review the elements and realign as needed. Because changing one element always has an effect on the other elements in the model, it is important that you continually review and adapt so that you don’t stagnate and lose market share.
For example, as your company grows, you may need to expand to other regions in the country or the world. Use the McKinsey 7S model to determine how these satellite sites will align with your goals and values. Will these regional locations be marketing, manufacturing, development, or sales sites?
As you work through different scenarios and change proposals, work with Lucidchart to create the visual charts and diagrams you will need to help people in your organization quickly assess and digest new information.

Looking for other ways to approach change management?
Explore other modelsAbout Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
The role of BAs in change management
Change is scary, and if managed poorly, it can lead to chaos. Learn how BAs play an important role in change management and see how they can deliver data and insights to help implement change successfully.
Using the ADKAR change management model
The ADKAR change model has been proven to help individuals understand change so companies can successfully innovate. Learn what ADKAR is and how to implement it.
What is change management?
When employees have an informed and accurate understanding of what changes are happening and how they affect them, they can become proponents of those changes—and that’s the kind of momentum any organization can benefit from.
7 fundamental change management models
Change management generally refers to how teams and companies implement organizational change. Learn 7 tried-and-true change management models that organizations return to again and again.

