It’s five times cheaper to keep an existing customer than to gain a new one. But how do you promote customer loyalty and retain your best customers?
Customer relationship management (CRM) helps businesses develop strategic processes to win the loyalty of their best customers and improve the buyer experience.
Here’s how.
What is CRM?
CRM stands for Customer Relationship Management. It is the foundational strategy a company uses to develop a customer-centric culture that focuses on managing and optimizing their current and future client relationships.
In short, companies that specialize in CRM help businesses analyze data about their customers’ interactions with the company in order to improve the value provided to customers and increase retention and profit.
In other words, CRM relies on a deep understanding of the customer (individually and collectively) in order to meet their needs, exceed their expectations, and deliver value. Ultimately, the companies that do this best will have an advantage over their competitors.
Note: The term CRM is also frequently used to describe the software or technology solutions that manage those relationships and enable CRM strategies. To avoid confusion, we will refer to this software as CRM software.
Purpose of CRM
The goal of any business is to generate profit from its products or services. To that end, the purpose of CRM is to optimize the relationship the company has with its strategically significant customers in order to maximize profits and build long-term success.
Strategically significant customers (SSCs) are a company’s most valuable clients. Generally speaking, SSCs make up only about 20% of the client base, but they generate 80% of the revenue. Because they generate more revenue, loyalty, and value than the average customer, they are an important part of any business’s strategy.
When it comes to CRM, strategically significant customers are a key focus. By capitalizing on the most valuable customer segments, companies can improve their long-term profitability and competitiveness.
Top 4 CRM models
There are several different strategies or models for customer relationship management. We’ll cover four of the most common CRM models briefly below.
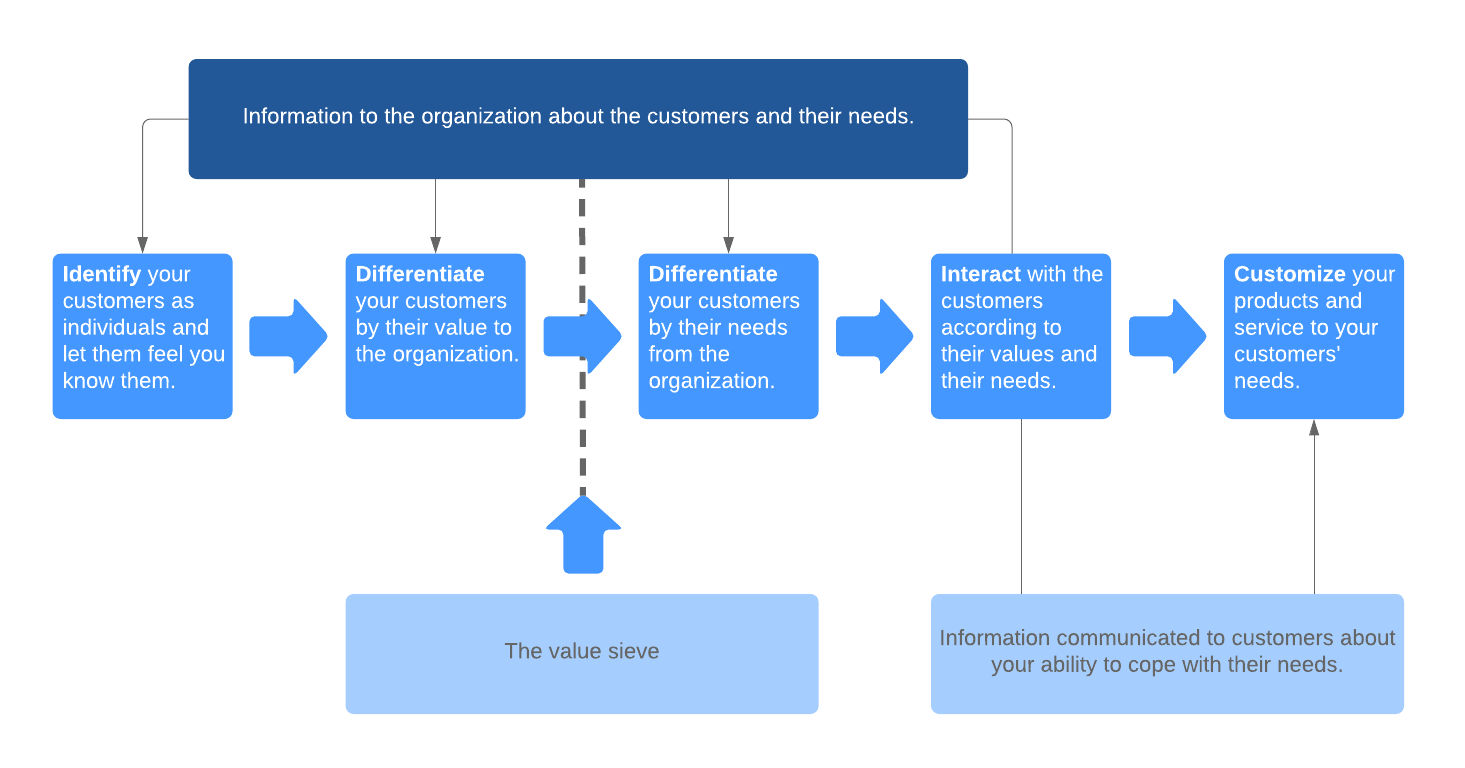
IDIC model
The IDIC model was developed by the Peppers and Rogers Group as a generic blueprint for implementing CRM in a variety of situations. IDIC stands for the four stages of CRM implementation: identify, differentiate, interact, and customize.
Identify
The first step of the IDIC model of CRM is to identify your customers. Businesses can accomplish this by collecting information like the customer’s name, address, and purchase history at each point of contact across the company.
The goal is to collect as much information or data as you can on each customer in order to better understand their needs, wants, and purchase behaviors.
Differentiate
The next step of the IDIC model is to differentiate or segment your customers based on their current and projected lifetime value. Remember: Not all customers will have the same value to the business.
By differentiating your customers based on their value to the company, you can prioritize your customer relationship efforts on the most valuable clients and tailor your interactions to best fit each segment for optimal profitability.
Interact
The third stage is where you get to apply your CRM plans for interacting with your customers. Once your customers are analyzed and categorized, you can develop customized interactions—for example, for valued customers, you might offer loyalty benefits or rewards to encourage retention and continued spending.
Keep in mind, you should be learning from each interaction to continually improve future interactions.
Customize
After you have documented your customer interactions, you can then analyze them to develop more customized one-to-one service. The goal is to ensure that your customers’ needs and expectations are met and that you have pinpointed them individually (or very narrowly).
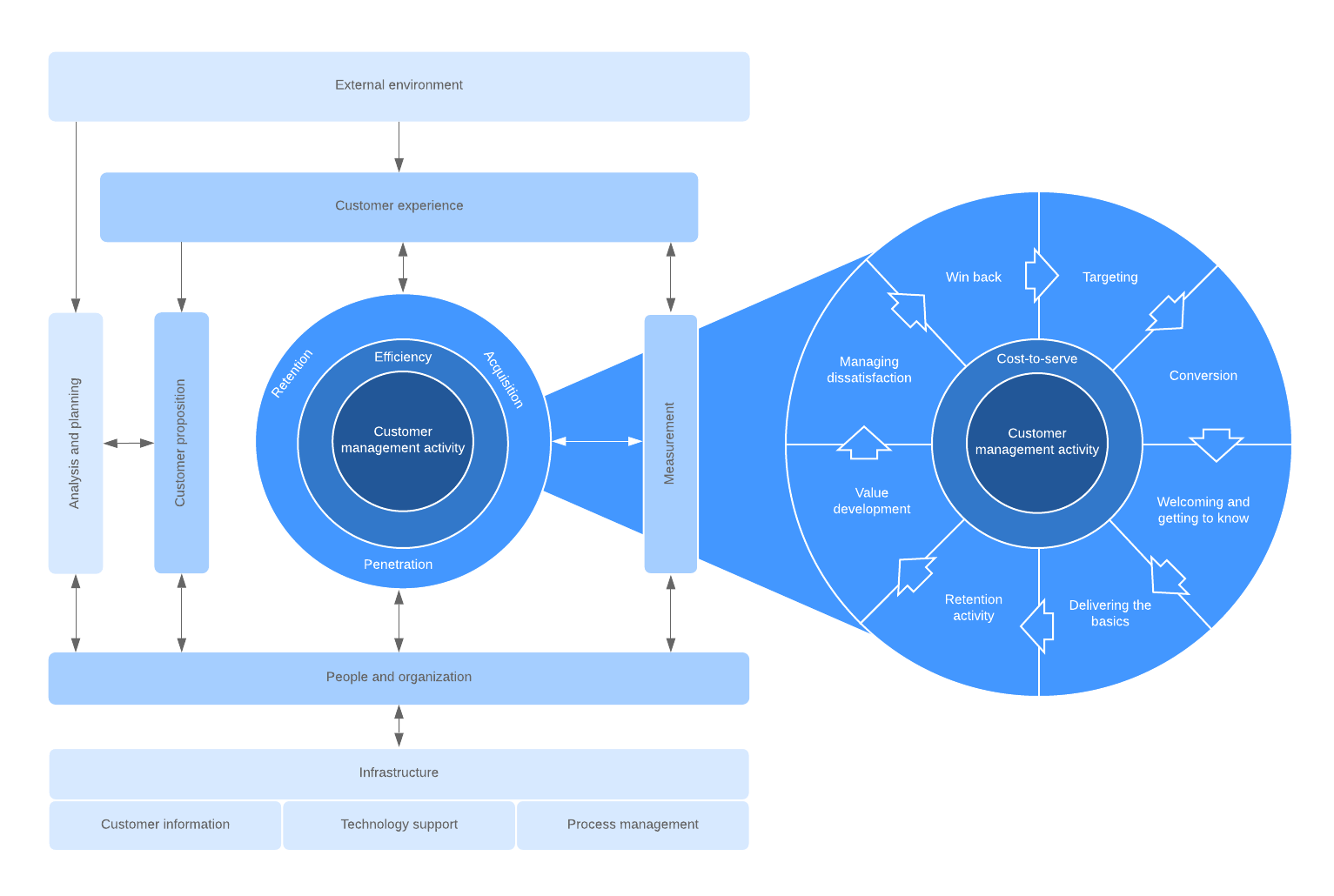
QCI model
Described as a customer management model rather than a customer relationship model, the Quality Competitive Index model focuses on three main activities: acquisition, retention, and penetration.
The QCI model starts with the customer’s external environment at the top—their pain points, business goals, and other factors will affect whether they are ready to buy or interact with your sales team, which in turn impacts the customer experience. The customer experience then affects customer proposition (what you offer the customer) and customer management activities. As you can see from the magnified version of the inner circle, many activities are involved to acquire and retain customers.
The QCI model also considers the people and technology involved with keeping this whole system going. Although QCI has replaced the word “relationship” in fraCRM, this framework of CRM still starts and ends with people.
Payne’s Five Process model
The Five Process CRM model was developed by Adrian Payne and Pennie Frow. This model of CRM emphasizes a cross-functional approach for effective CRM processes.
There are two main components to the model: cross-functional CRM processes and key elements of CRM implementation.
Payne’s model outlines five processes:
- Strategy development
- Value creation
- Multichannel integration
- Information management
- Performance assessment
There are four key elements necessary for a successful CRM implementation:
- CRM readiness
- CRM change management
- CRM project management
- Employee management
When implementing a CRM strategy, companies should conduct a CRM readiness assessment to determine how prepared they are to implement a new CRM process.
Additionally, because CRM involves a fundamental cultural and operational shift, companies should invest in CRM change management and project management as the new strategies are introduced and the complexities of the CRM initiatives grow.
Finally, employee buy-in is crucial for successful CRM. Make sure your employees understand the strategies and processes and engage with the new customer-centric culture.
Without these underlying conditions and elements, the CRM processes cannot succeed.
CRM value chain
A value chain is a high-level model developed by Michael Porter that identifies the processes a business uses to develop an end product or service for the customer. The goal of the value chain model is to identify and prioritize the most valuable activities to the company and improve processes to gain a competitive advantage.
The CRM value chain model applies this principle to customer relationships. This CRM model observes all the stages and activities required to build a relationship with a customer.
These activities are divided into two stages: primary and support.
Primary stage
The primary stage of CRM value chain has five main processes that enable the strategy.
-
Customer portfolio analysis: Similar to the IDIC model, the first step of the value chain model is to analyze your customers to identify your SSCs (a.k.a. the customers who create the most value for the company). This analysis stage helps companies understand their customers so they can better address their needs and expectations and develop strategies to maximize their lifetime value.
-
Customer intimacy: The next step is to engage with the customer and build on the original database of information. At each touchpoint, companies should be collecting data on the interaction in order to better understand and serve their customer. The better you know your customer (and adjust your service accordingly), the more likely you are to retain their business over the long term.
-
Network development: A business’s network includes all people and entities involved in the value chain, including partners, suppliers, customer service, investors, etc. The goal is to use your customer data to inform the processes at each level of your network so that the entire system works together to optimize your customer’s experience.
-
Value proposition development: Armed with your customer information and interaction data, you can create value for your target customers. The idea is to shift the focus from the product to your service and to reduce process costs to create more value for the customer.
-
Relationship management: The last stage of the value chain model is to manage your customer lifecycle. This process involves evaluating your business processes and organizational structure to manage acquisition, retention, and customer development.
Support stage
There are five supporting conditions necessary in order to effectively implement the strategic processes of the primary stage:
- Leadership and culture
- Procurement processes
- HR management processes
- IT/data management processes
- Organization design
Creating and developing these underlying conditions will support a successful CRM value chain implementation.
Using Lucidchart to model your CRM strategy
Building a loyal customer base is key to growing a sustainable business. In fact, just a 5% increase in customer retention can result in 25% higher profits. But CRM is a big undertaking. Keeping track of all your processes and data can be overwhelming. Luckily, Lucidchart can help.
Lucidchart is a cloud-based diagramming solution that makes it easy to create streamlined flowcharts and diagrams.
Use Lucidchart to visualize your CRM model, document your processes, and even map out your sales org design. Lucidchart also integrates with Salesforce so you can import your schema directly into your document to visualize your data—complete with the official Salesforce shape library—and make connections more easily.

See how Lucidchart can improve sales operations and help your team close bigger deals faster.
Sign up freeAbout Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How to structure your sales organization for success
The way you structure your sales organization can have lasting consequences for your business’s long-term success. Take a look at three common sales team models as well as best practices for creating a successful organization.
Crossing the CRM Rubicon: Building a Sales Organization Part II
We’re excited to roll out the second half of our series on the key role process plays in building a sales organization. You’ve heard about “Crossing the Chasm,” but what about “Crossing the Rubicon”?