
Why You Should Use the Critical Path Method
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 4 min
Topics:
Critical Path Method
If your team is like most, it has several projects competing for attention with multiple contingencies and fixes looming on the horizon. The critical path method, or CPM, prioritizes the most crucial tasks first to keep projects in line and on time.
In 1984’s The Goal, a staple in the world of business management, Eli Goldratt tells a story about a scout troop out on a hike.
The group quickly learned that, no matter how fast some of the scouts could hike, the troop couldn’t reach their destination any faster than the slowest scout, Herbie, could go. So they put Herbie in front and helped him hike the best he could.
One big takeaway from this story? You have to determine the dependencies of a project (your Herbie) before you can figure out exactly how long the project will take.
With the critical path method, you can better manage projects and anticipate timelines by finding which tasks depend on the completion of other tasks and outlining the fastest way to the end of your project.
What is critical path method?
If your team is like most, it has several projects competing for attention with multiple contingencies and fixes looming on the horizon. Often used along with PERT charts, the critical path method, or CPM, prioritizes the most crucial tasks first to keep projects in line and on time.
Since the 1950s, critical path project management has provided the ability to outline a project’s longest sequence of tasks, referred to as the critical path, so project managers can determine the minimum amount of time a project will take. So how do you go about finding it?
6 steps to finding the critical path
You can find the critical path of any project by completing the following six steps.
Step 1: Establish each activity
Create a diagram to identify all the deliverables within a project. A reliable way to do this is with a work breakdown structure. A work breakdown structure helps you pinpoint all the tasks in a project, making it both more manageable and measurable.
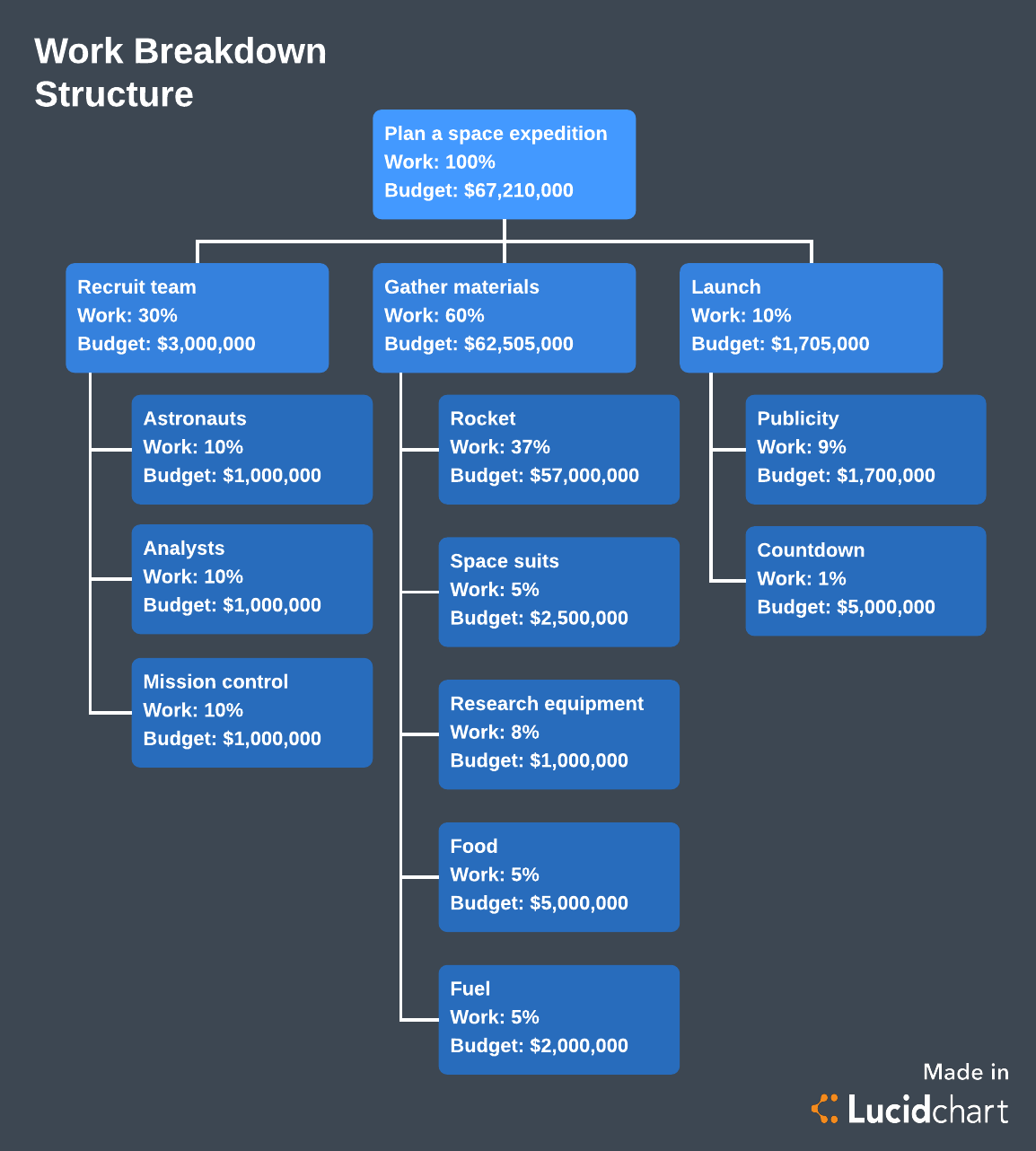
If the template above isn’t enough to get you started, see our complete instructions for how to create a work breakdown structure.
Step 2: Define the activity sequence
Project deliverables can be like dominos—ones farther along the path depend upon their counterparts falling first. List the proper order of tasks, considering with each activity the task that has to take place before it. A crucial step in the critical path method, streamlining the sequence of tasks is paramount in avoiding possible delays.
Step 3: Create the activity network diagram
The next step along your journey to the critical path is creating the activity network diagram, or critical path analysis chart (also known as the CPA). The purpose of the network diagram is to illustrate not only all of the project’s deliverables, but also the dependencies that you determined in the previous step.
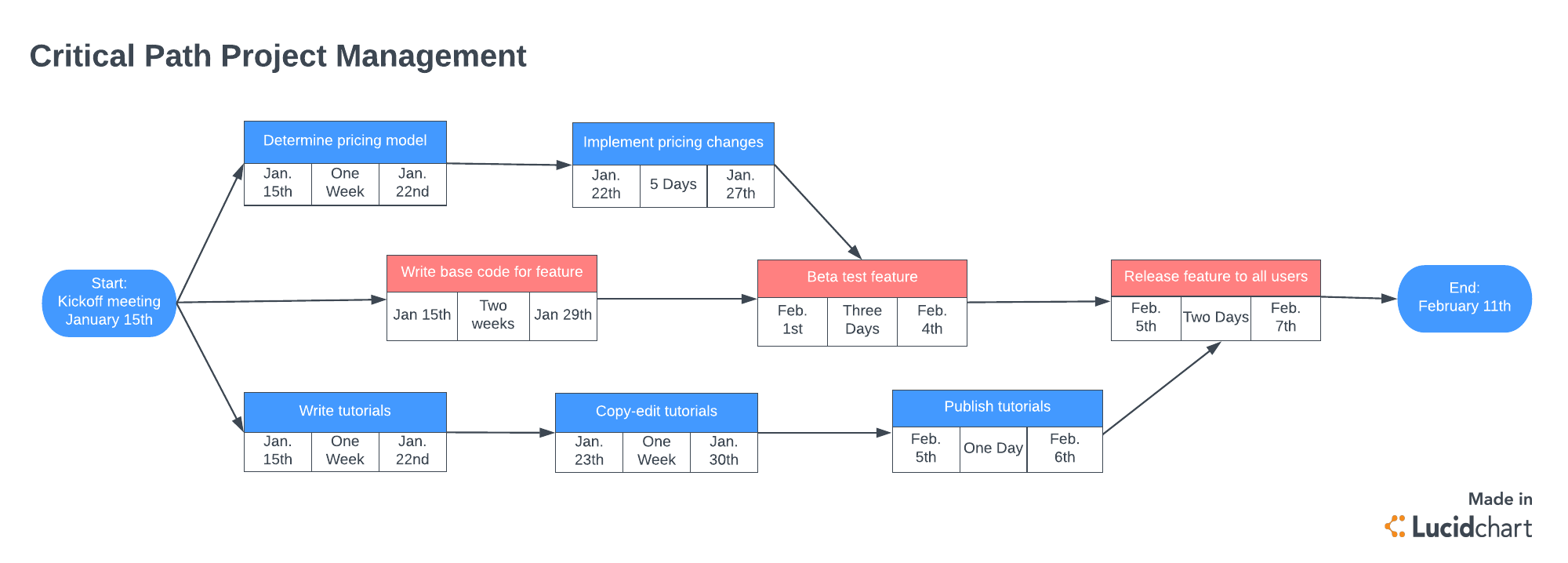
Step 4: Determine the activity completion time
The last step before identifying the critical path is estimating the completion time for each task. You can calculate these times based on past experience or an estimation from your team members—some project managers use a three-point estimation to feel more confident. This is the last missing piece and the crux of CPM.
Step 5: Identify the critical path
Correctly identifying the critical path is completely contingent upon the previous step. Without accurate completion times, there’s no way to get a full picture of a project’s actual scope. Looking at your project network diagram, you can easily scan for the critical path, or the amount of time needed for your project based on the longest sequence of deliverables.
This step will also show whether your project has competing critical paths. If it does, the critical path might change once the project has begun, which increases the chance of a change in schedule.
Step 6: Update the critical path progress
With the blueprints of your project in place, all that’s left to do now is to continue updating your network diagram as you complete tasks with their actual completion times. By keeping your diagram up to date, you can evaluate if your project is on time and whether you need to make any adjustments.
Visualizing the ins and outs of a project using the critical path method will give you and your team a better understanding of how long tasks will actually take to complete and how every piece—and teammate—is dependent on each other to succeed.
With Lucidchart, you can create your own work breakdown structures and project network diagrams, and as you do, you’ll find the path that will make all the difference.
Sign up today and map out all your processes and timelines.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How to create a work breakdown structure and why you should
In project management, WBS stands for work breakdown structure. This foundational tool breaks a project or objective down into smaller, more manageable pieces so you can plan, manage, and evaluate large projects. Learn how to create a work breakdown structure and use our free templates!
What your boss would like to know about project network diagrams
Project network diagrams allow PMs to summarize their plans in one visual that can be easily digested and understood. Learn how to make one here.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy.