4 phases of rapid application development methodology
Reading time: about 6 min
In the world of project management, “agile” is the method du jour.
For decades, project management teams clung to the traditional approach of strict planning, process, and documentation. Agile management turns this approach on its head, and it’s no wonder that this methodology has become more popular over time. According to a 2017 study from PwC, agile projects are 28% more successful than traditional projects.
And project managers have taken notice—particularly among teams in industries like software development where technology, objectives, and targets are in constant flux.
So what is rapid application development?
Rapid application development (RAD) is an agile project management strategy popular in software development.
The key benefit of RAD methodology is fast project turnaround, making it an attractive choice for developers working in a fast-paced environment like software development. This rapid pace is made possible by RAD’s focus on minimizing the planning stage and maximizing prototype development.
By reducing planning time and emphasizing prototype iterations, RAD allows project managers and stakeholders to accurately measure progress and communicate in real time on evolving issues or changes. This results in greater efficiency, faster development, and effective communication.
You can break down the process in a few ways, but in general, the RAD process follows four main phases.
Phase 1: Requirements planning
This phase is equivalent to a project scoping meeting. Although the planning phase is condensed compared to other project management methodologies, this is a critical step for the ultimate success of the project.
During this stage, developers, clients (software users), and team members communicate to determine the goals and expectations for the project as well as current and potential issues that need to be addressed during the build.
A basic breakdown of this stage involves:
- Researching the current problem
- Defining the requirements for the project
- Finalizing the requirements with each stakeholder’s approval
Everyone should have the opportunity to evaluate the goals and expectations for the project and weigh in. By getting approval from each key stakeholder and developer, teams can avoid miscommunications and costly change orders down the road.
Phase 2: User design
Once the project is scoped out, it’s time to jump right into development and build out the user design through various prototype iterations.
This is the meat and potatoes of the RAD methodology—and what sets it apart from other project management strategies. During this phase, clients work hand-in-hand with developers to ensure their needs are met at every step in the design process. It’s almost like customizable software development where the users can test each prototype of the product, at each stage, to ensure it meets their expectations.
All the bugs and kinks are worked out in an iterative process. The developer designs a prototype, the client tests it, and then they come together to communicate on what worked and what didn’t.
This method gives developers the opportunity to tweak the model as they go until they reach a satisfactory design.
Both the software developers and the clients learn from the experience to make sure nothing slips through the cracks.
Phase 3: Rapid construction
Phase 3 takes the prototypes and beta systems from the design phase and converts them into the working model.
Because the majority of the problems and changes were addressed during the thorough iterative design phase, developers can construct the final working model more quickly than they could by following a traditional project management approach.
The phase breaks down into several smaller steps:
- Preparation for rapid construction
- Program and application development
- Coding
- Unit, integration, and system testing
The software development team of programmers, coders, testers, and developers work together during this stage to make sure everything works smoothly and that the end result satisfies the client’s expectations and objectives.
This third phase is important because the client still gets to give input throughout the process. They can suggest alterations, changes, or even new ideas that can solve problems as they arise.
Phase 4: Cutover
This is the implementation phase, where the finished product goes to launch. It includes data conversion, testing, and changeover to the new system, as well as user training.
All final changes are made while the coders and clients continue to look for bugs in the system.
Benefits of RAD methodology
RAD is one of the most successful software development programs available today, with numerous benefits for both software development teams as well as their clients.
Here are just a few advantages:
- RAD lets you break the project down into smaller, more manageable tasks.
- The task-oriented structure allows project managers to optimize their team’s efficiency by assigning tasks according to members’ specialties and experience.
- Clients get a working product delivered in a shorter time frame.
- Regular communication and constant feedback between team members and stakeholders increases the efficiency of the design and build process.
With a shorter planning phase and a focus on highly iterative design and construction, RAD teams are able to accomplish more in less time without sacrificing client satisfaction.
This is a win-win for both project managers and clients.
Is the RAD model right for your team?
That depends.
RAD methodology can be an effective strategy for a number of different projects and teams, but you should consider the following key factors before you implement it.
Do you have a knowledgeable and experienced team of developers, coders, and engineers who can dedicate themselves to this ongoing development process?
The RAD process is intensive and requires an all-hands-on-deck mindset from your team.
Is your client open and committed to following this approach?
Without client buy-in from the start, your project is more likely to fail due to communication breakdowns.
Is your client willing to commit to the determined schedule for the model completion?
The RAD approach differs from traditional methodology by adhering to a strict deadline. In order for the project to proceed successfully, all stakeholders should be on board with the timeline.
Do you have the right tools and software to effectively apply this methodology?
The success of RAD depends on a project manager’s ability to fully outline each development phase and communicate effectively with team members and stakeholders in real time.
Lucidchart makes this possible—our intuitive visual collaboration platform allows you to map out every step of the process, from scoping to building. With intuitive drag-and-drop functionality, you can quickly create user flow diagrams that explain the functionality of the app, workflows that will ensure your team understands the workflow and its individual responsibilities, and many more powerful visuals.
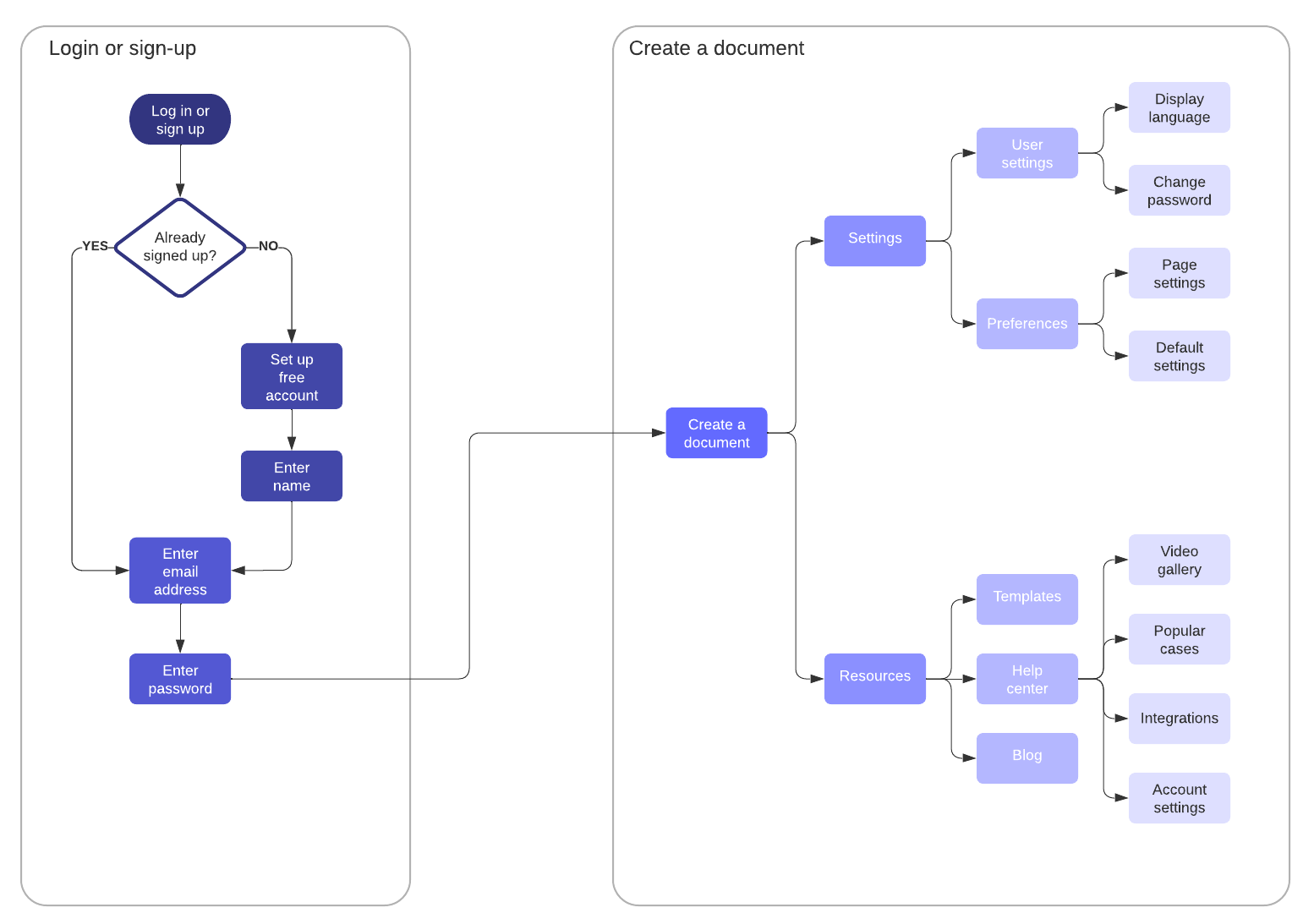
Whether you’re a die-hard fan of all things agile, or you’ve just jumped on the bandwagon, there’s no doubt that with the right team and committed stakeholders, the agile RAD model can improve project efficiencies, produce deliverables on schedule, and increase client satisfaction.

Lucidchart that has the flexibility and usability to keep you and your team on task and on point from start to finish.
Sign up freeAbout Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
What is Adaptive Project Framework?
Adaptive Project Framework (APF) is a project management methodology that prepares teams to anticipate change and respond. Learn the five phases of APF and determine whether it's a good fit for your team.
What is Agile methodology? (+ how you're already using it)
Learn about Agile methodology and the ways you can apply these principles as a product manager. Template examples of Agile frameworks included!
