In recent years, we have been in the midst of a rapidly growing Software as a Service (SaaS) boom. As more executives and organizations recognize the benefits of SaaS, the development of traditional “on-premises” enterprise software is expected to decline. As of 2023, 70% of organizations reported that more than half of their infrastructure is in the cloud.
So if you have landed in an organization that offers cloud-based software solutions as a service, it is important that you have a well-defined and planned-out SaaS sales process to successfully sell those services.

SaaS sales definition
So what is SaaS sales?
In simple terms, SaaS sales is the process of selling your company’s web-based software to clients. Your clients may include individuals as well as other organizations and companies. Business-to-Business (B2B) focuses on selling services to other companies rather than individuals.
Salespeople who sell SaaS focus on acquiring new customers and retaining or upselling current customers. It is important that your salespeople clearly communicate the benefits and features of your product. They must also be very well versed with the software so demonstrations run smoothly and so they can answer customer questions.
A brief history of SaaS
You may be surprised to learn that centralized hosting of business applications dates back to the ’60s. Companies like IBM provided mainframes and offered services that included computing power and database storage to banks and other large organizations.
In the ’90s, the popularity and expansion of the Internet brought a new class of centralized computing called application service providers (ASP). An ASP provided individuals or enterprises access to applications and services over a network, usually a local area network (LAN) or a LAN with access to the Internet.
Software as a Service is basically an extension of ASP. However, with ASP, the focus was mainly on hosting third-party applications. With SaaS, vendors typically develop and manage their own centrally hosted applications.
SaaS sales models: Which is right for you?
Imagine that you're on a hike, and you find a shortcut that gets you to your destination faster than if you had stayed on the marked path. In your excitement, you probably tell all your friends about how much more efficient the shortcut is. As more people learn of your shortcut, they will travel the path until the shortcut becomes the new “official” path. Some people may branch off onto other paths in search of another shortcut or in an effort to find different and more interesting scenery.
Just like there are several paths to take when you go hiking, there is not just one “right” SaaS sales model that leads to success. Deciding on the SaaS sales strategy that will work for you depends on where your company currently is in its SaaS adoption and development. For example, if you are a startup or an established company that has never developed cloud-based software, you may want to look at some startup SaaS and B2B software sales strategies that have worked for other companies.
Selecting the right SaaS sales model will tell you how many salespeople you need to hire, how you will contact and interact with customers, who your potential customers are, and how you can successfully close the deal.
The following are three common SaaS sales models that you can choose from to help you plan your strategy. Each model considers price and complexity—more complex services have a higher price than less complex services.
Customer self-service
This model has the potential to generate significant revenue while keeping costs low. In a self-service model, customers understand the value of your product, how to buy it, and how to use it without consulting a salesperson or customer service rep.
The self-service model keeps the price and complexity low because you don’t have to hire as many developers to create the product or salespeople to sell it. However, in order to reach your revenue goals, your sales volume will need to be very high.
Characteristics of customer self-service models include:
- Sales: Involves little or no sales.
- Marketing: Creates awareness through easily accessible educational content and automation that drives the entire purchase process.
- Support: Includes automation and tools for easy onboarding and updating. In addition, templates and educational content allow customers to resolve issues on their own.
Transactional sales
This sales model raises complexity and price. You may need to hire more people to develop and sell the product, increasing your costs. As the price increases, your customers’ expectations increase. Before parting with their money, they may want to ensure that there will be more of a business relationship.
The transactional sales model is characterized by efficient, high-volume sales and support operations, short sales cycles, and rapid onboarding. Customers may expect to sign contracts, receive periodic updates, comprehensive documentation, and access to service reps when problems arise.
Transactional sales models tend to be high-risk and high-reward with a higher volume of sales. Characteristics of this model include:
- Sales: Inside sales reps are supported by online content and automation. Additional tools, training, incentives, and metrics increase efficiency and transactions per sales rep.
- Marketing: Highly qualified leads are fed to the sales team to build a pipeline and improve efficiency. Educational content and automation are marketing trends that remove complexity from the purchase.
- Support: In addition to customer self-service tools, templates, and educational content, customers have access to customer service representatives as needed.
In either the customer self-serve or transactional sales models, it’s important to visualize your efforts to ensure that you provide a seamless buyer experience. Using a visual diagramming software like Lucidchart, you can easily create and collaborate on customer journey maps, process flowcharts, email flows, GTM plans, content marketing funnels, and other visuals to better understand and improve the SaaS sales process.
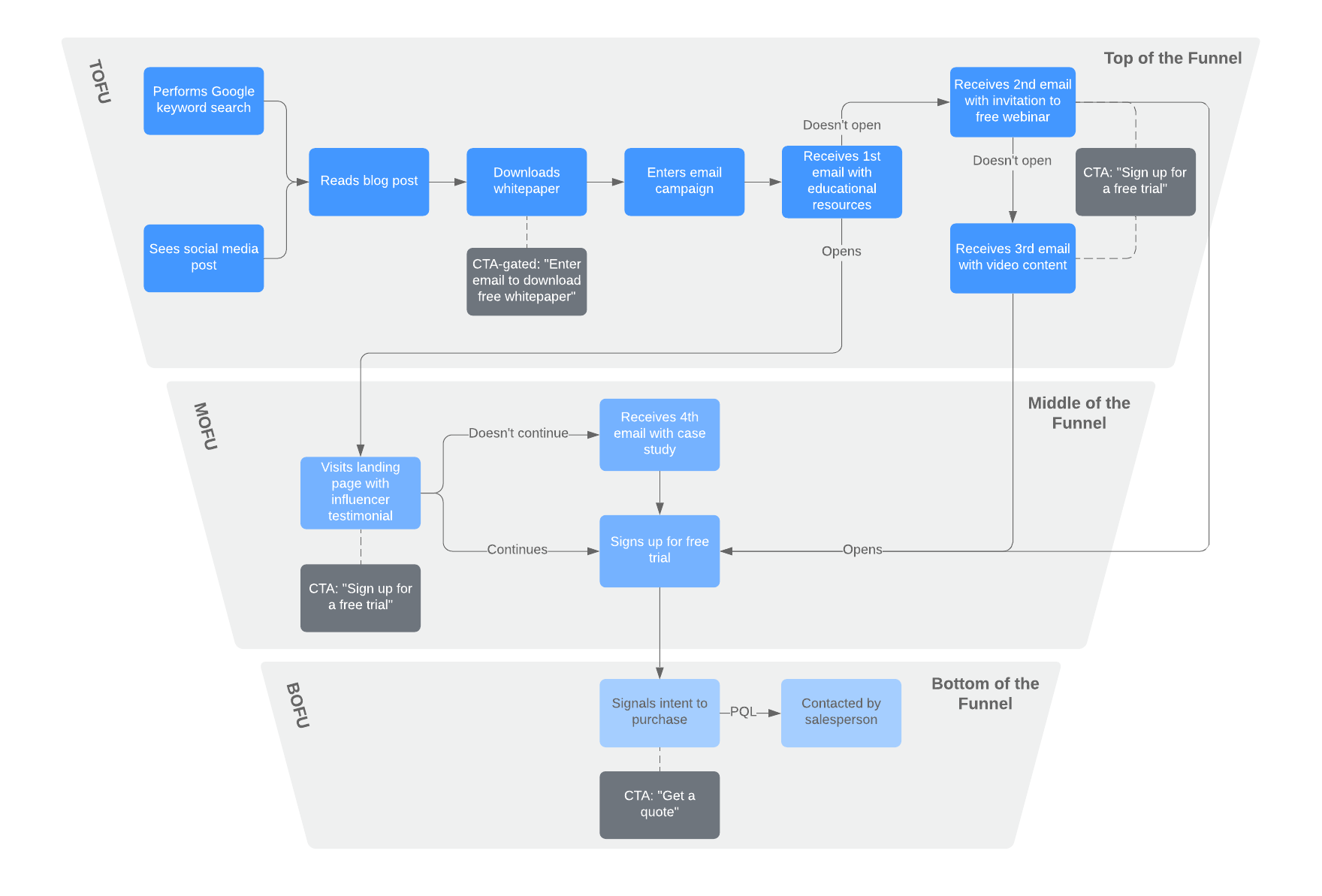
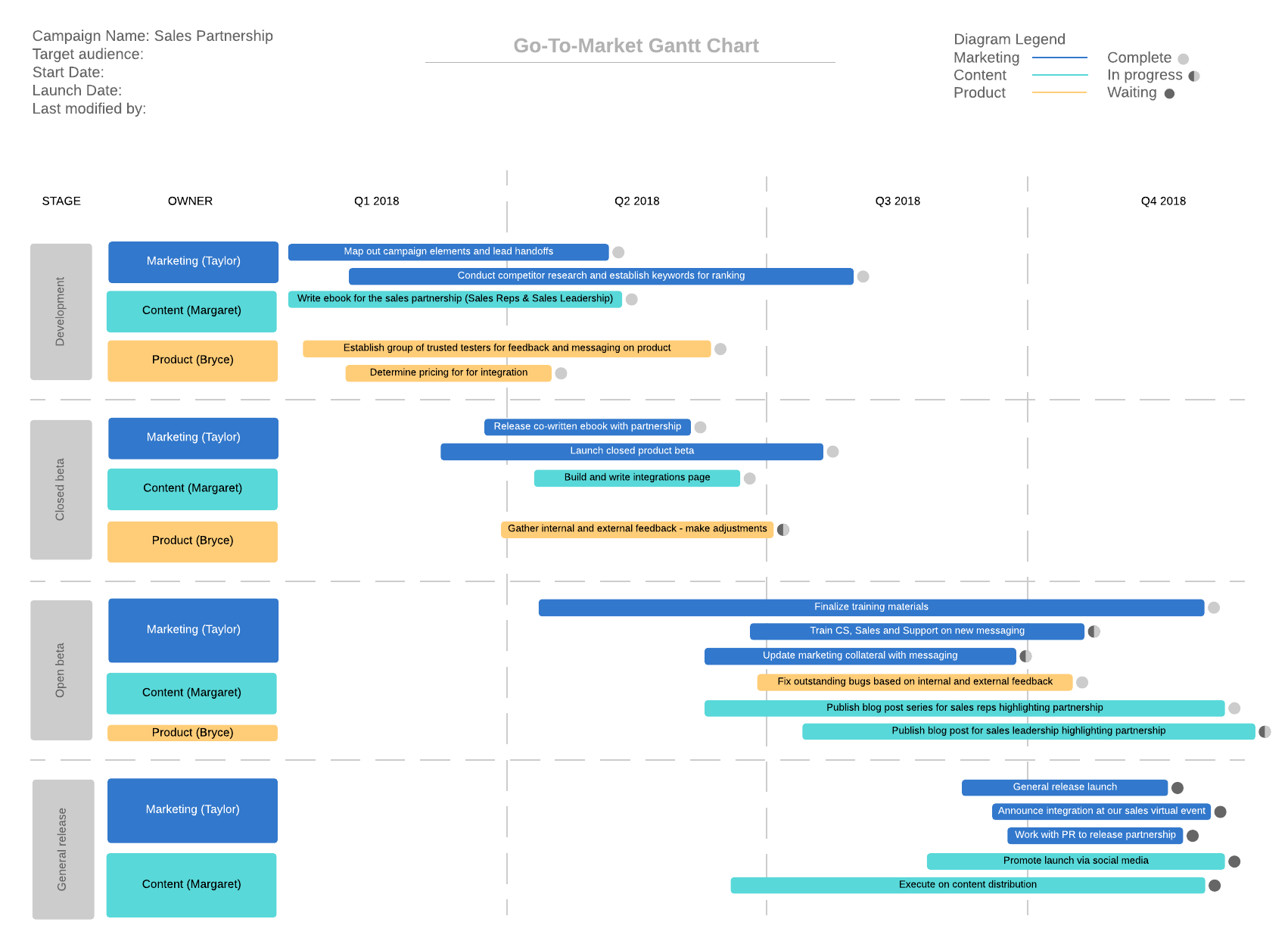
Enterprise sales
As the name implies, this model is intended for B2B enterprise sales. Offerings tend to be very complex and include a feature-rich suite of solutions that address strategic, core business processes. These products and services tend to offer so much value that the natural target audience is mid-to-large enterprises.
Characteristics of this model include:
- Sales: Territory sales reps focus on a narrow set of target prospects, which are directly supported by product marketing and sales engineering resources.
- Marketing: Relationship-building, trust, education, and brand awareness is dealt with through high-end marketing. More complex sales tools such as product roadmaps and ROI calculators are used to more efficiently target and acquire potential customers.
- Support: High-priority technical and sales support, including onsite issue resolution, in addition to hands-on training and other educational tools tailored to the specific needs of the customer.
The path to selling SaaS isn’t typically linear, particularly for enterprise sales. In the past, salespeople could sway a single person to close the deal, but now they have to create a consensus among a group of decision-makers with buying power.
Creating an account map can be a helpful way to navigate who owns which account so that you can effectively manage your SaaS sales process. They will help reps identify key decision-makers and determine the best path to sale.
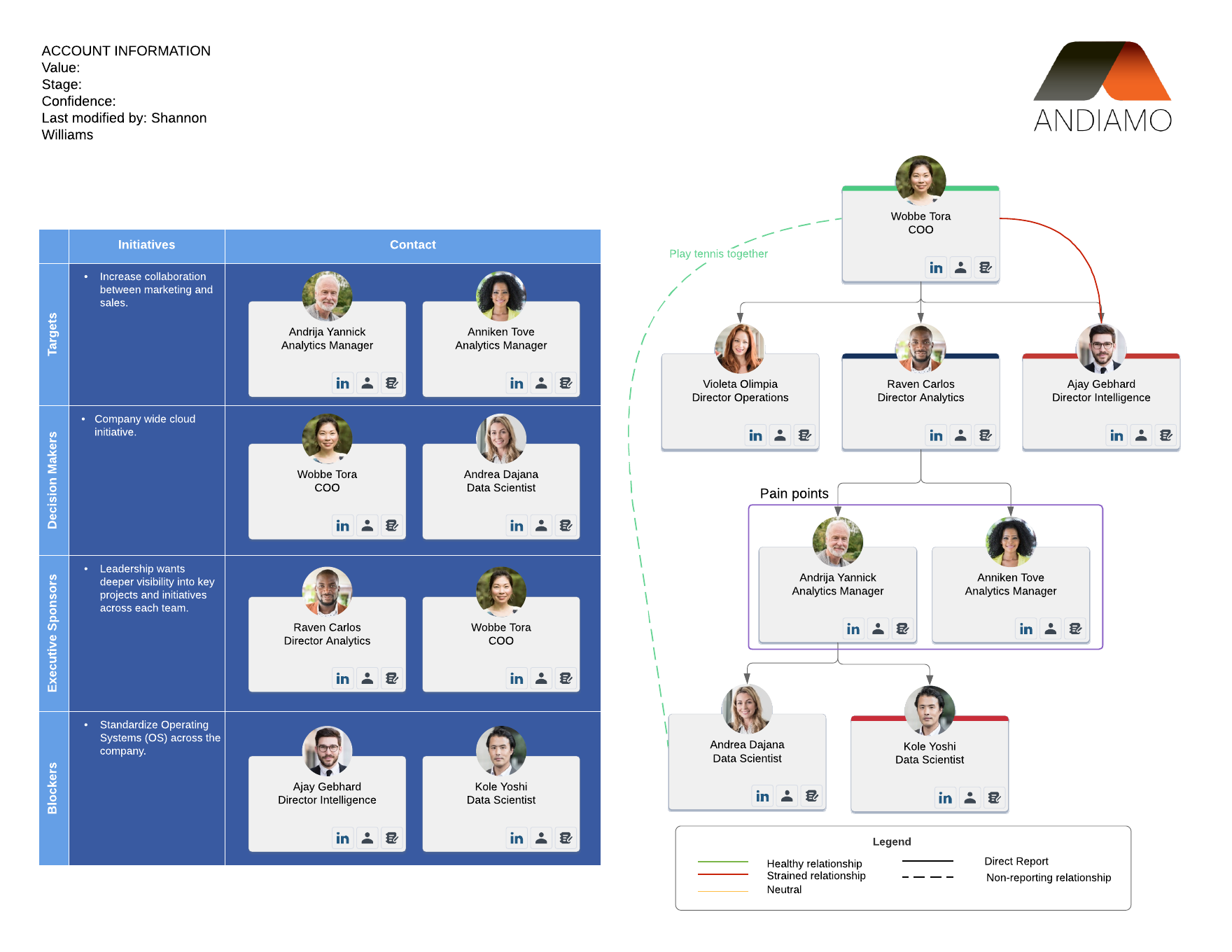
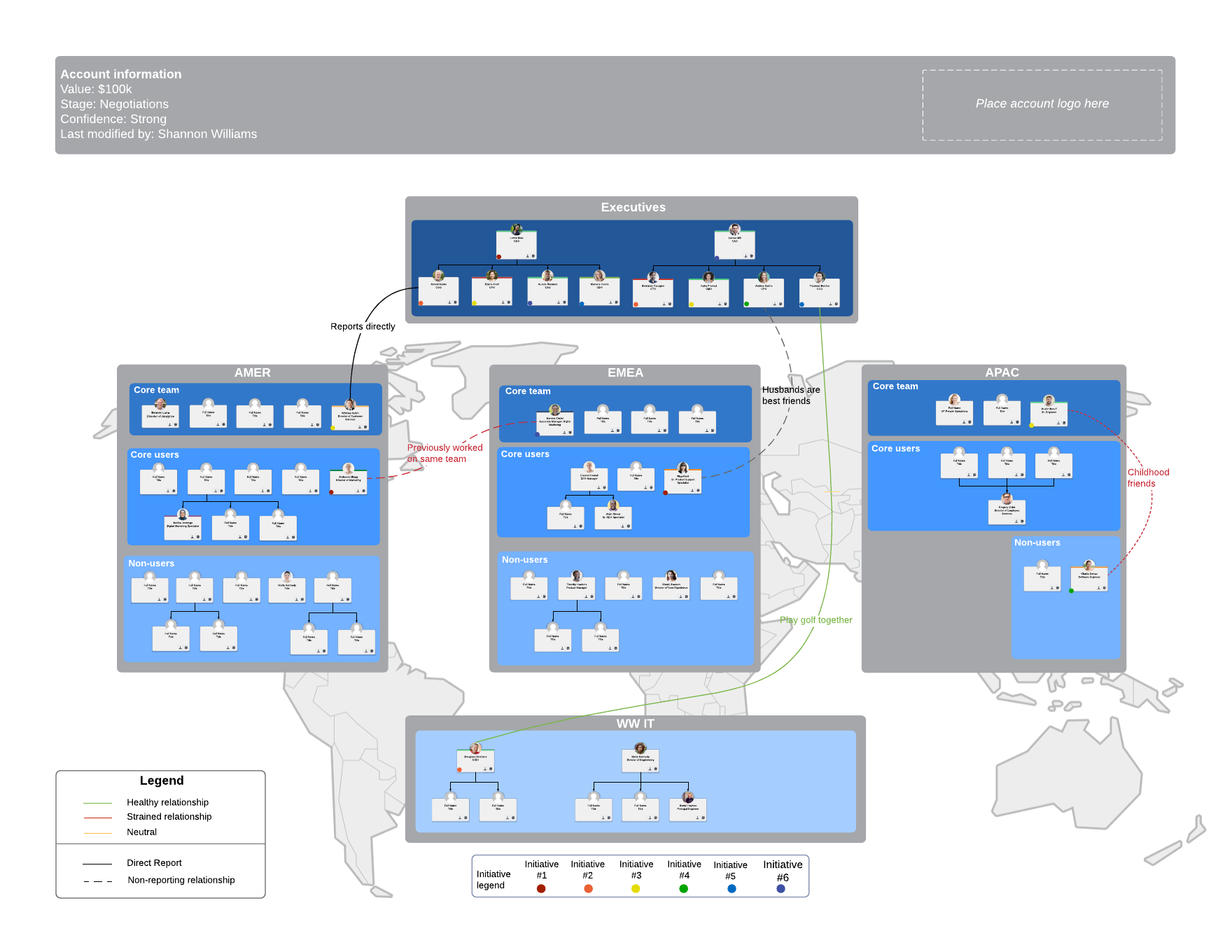

Learn how account maps can become a pivotal part of your SaaS sales process.
See the benefitsAbout Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How to build an account map
Sales account maps help you get the most from your data by filling in the gaps and connecting the dots throughout the sales cycle. Learn how and why you should be using them.
How to digitally walk the sales floor with actionable account maps
Learn how to “digitally” walk your sales floor so you can manage deals at scale and stay up to date on the team’s progress.
What is B2B2C? How the B2B2C business model works and benefits companies
B2B2C stands for business to business to consumer. Learn how it differs from B2B and how Lucidchart can help you implement it.

